You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003520_00608
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003520_00608
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | RC9 sp900769145 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; UBA932; RC9; RC9 sp900769145 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003520_00608 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 38335; End: 40767 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 488 | 744 | 1.8e-40 | 0.8669354838709677 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd16027 | SGSH | 5.01e-134 | 46 | 459 | 1 | 373 | N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase (SGSH; sulfamidase). N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase (SGSH) belongs to the sulfatase family and catalyses the cleavage of N-linked sulfate groups from the GAGs heparin sulfate and heparin. The active site is characterized by the amino-acid sequence motif C(X)PSR that is highly conserved among most sulfatases. The cysteine residue is post-translationally converted to a formylglycine (FGly) residue, which is crucial for the catalytic process. Loss of function of SGSH results a disease called mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA (Sanfilippo A syndrome), a fatal childhood-onset neurodegenerative disease with mild facial, visceral and skeletal abnormalities. |
| cd08986 | GH43-like | 6.08e-107 | 489 | 747 | 1 | 252 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein; uncharacterized. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43)-like subfamily includes uncharacterized enzymes similar to those with beta-1,4-xylosidase (xylan 1,4-beta-xylosidase; EC 3.2.1.37), beta-1,3-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.-), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), arabinanase (EC 3.2.1.99), xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8), endo-alpha-L-arabinanase and galactan 1,3-beta-galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.145) activities. These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many of the enzymes in this family display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd16031 | G6S_like | 6.42e-76 | 44 | 456 | 1 | 428 | unchracterized sulfatase homologous to glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase(G6S, GNS). N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase also known as glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase hydrolyzes of the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-sulfate units of heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate. Deficiency of N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase results in the disease of Sanfilippo Syndrome type IIId or Mucopolysaccharidosis III (MPS-III), a rare autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease. |
| cd16033 | sulfatase_like | 6.20e-66 | 46 | 463 | 1 | 411 | uncharacterized sulfatase subfamily. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters from wide range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. The biological roles of sulfatase includes the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodeling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. The sulfatases are essential for human metabolism. At least eight human monogenic diseases are caused by the deficiency of individual sulfatases. |
| cd16022 | sulfatase_like | 1.60e-62 | 46 | 329 | 1 | 236 | sulfatase. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters from wide range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. The biological roles of sulfatase includes the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodeling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. The sulfatases are essential for human metabolism. At least eight human monogenic diseases are caused by the deficiency of individual sulfatases. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAD72594.1 | 3.10e-161 | 22 | 801 | 724 | 1607 |
| AWW33023.1 | 1.86e-135 | 477 | 801 | 31 | 373 |
| QDU39553.1 | 4.31e-135 | 44 | 801 | 29 | 1022 |
| AGA79989.1 | 2.92e-134 | 479 | 801 | 33 | 373 |
| QXD22573.1 | 3.81e-134 | 476 | 801 | 67 | 402 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4MHX_A | 2.07e-37 | 47 | 464 | 24 | 478 | ChainA, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MHX_B Chain B, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MIV_A Chain A, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MIV_B Chain B, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MIV_C Chain C, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MIV_D Chain D, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MIV_E Chain E, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MIV_F Chain F, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MIV_G Chain G, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens],4MIV_H Chain H, N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase [Homo sapiens] |
| 7STT_A | 4.16e-34 | 45 | 460 | 6 | 435 | ChainA, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Pedobacter yulinensis],7STU_A Chain A, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Pedobacter yulinensis],7STV_A Chain A, N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase [Pedobacter yulinensis] |
| 5G2V_A | 9.72e-30 | 39 | 487 | 22 | 526 | Structureof BT4656 in complex with its substrate D-Glucosamine-2-N, 6-O-disulfate. [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 1E1Z_P | 1.64e-25 | 46 | 455 | 3 | 449 | Crystalstructure of an Arylsulfatase A mutant C69S [Homo sapiens] |
| 1E3C_P | 1.64e-25 | 46 | 455 | 3 | 449 | Crystalstructure of an Arylsulfatase A mutant C69S soaked in synthetic substrate [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2KN71 | 2.33e-56 | 44 | 463 | 45 | 448 | Ulvan-active sulfatase OS=Formosa agariphila (strain DSM 15362 / KCTC 12365 / LMG 23005 / KMM 3901 / M-2Alg 35-1) OX=1347342 GN=BN863_22010 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P51688 | 1.01e-36 | 47 | 464 | 24 | 478 | N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=SGSH PE=1 SV=1 |
| T2KN90 | 1.81e-36 | 44 | 478 | 48 | 510 | Ulvan-active sulfatase OS=Formosa agariphila (strain DSM 15362 / KCTC 12365 / LMG 23005 / KMM 3901 / M-2Alg 35-1) OX=1347342 GN=BN863_22210 PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q89YS5 | 4.95e-29 | 36 | 487 | 43 | 550 | N-acetylglucosamine-6-O-sulfatase OS=Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (strain ATCC 29148 / DSM 2079 / JCM 5827 / CCUG 10774 / NCTC 10582 / VPI-5482 / E50) OX=226186 GN=BT_4656 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P15289 | 4.47e-24 | 46 | 455 | 21 | 467 | Arylsulfatase A OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=ARSA PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
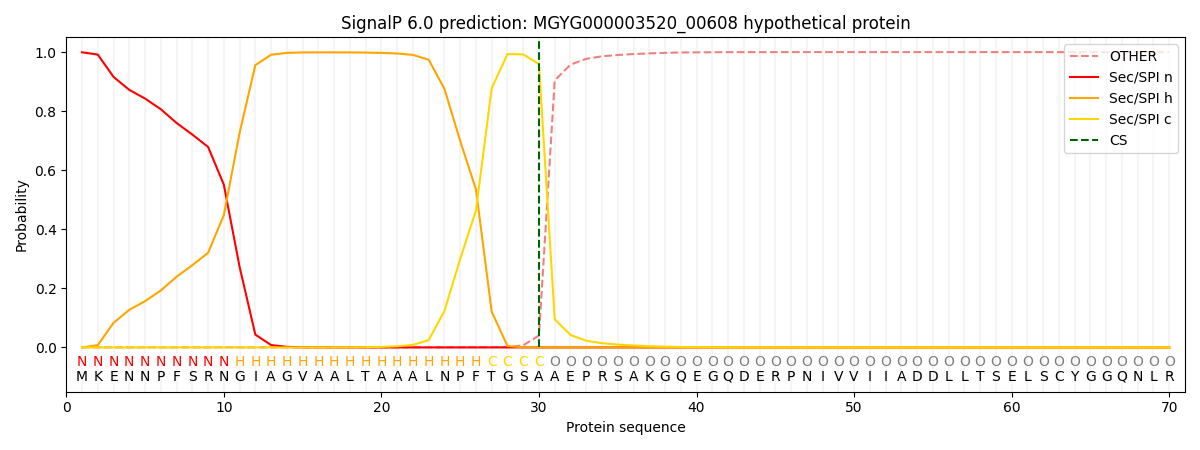
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.001022 | 0.997375 | 0.000270 | 0.000843 | 0.000255 | 0.000202 |
