You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003590_01818
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003590_01818
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Sodaliphilus sp900770215 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Muribaculaceae; Sodaliphilus; Sodaliphilus sp900770215 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003590_01818 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH171 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 50653; End: 51903 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH171 | 65 | 414 | 7.1e-113 | 0.9971830985915493 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam07075 | DUF1343 | 7.05e-170 | 66 | 414 | 1 | 362 | Protein of unknown function (DUF1343). This family consists of several hypothetical bacterial proteins of around 400 residues in length. The function of this family is unknown. |
| COG3876 | YbbC | 5.60e-92 | 55 | 414 | 36 | 409 | Uncharacterized conserved protein YbbC, DUF1343 family [Function unknown]. |
| cd05243 | SDR_a5 | 0.002 | 72 | 244 | 8 | 178 | atypical (a) SDRs, subgroup 5. This subgroup contains atypical SDRs, some of which are identified as putative NAD(P)-dependent epimerases, one as a putative NAD-dependent epimerase/dehydratase. Atypical SDRs are distinct from classical SDRs. Members of this subgroup have a glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif that is very similar to the extended SDRs, GXXGXXG, and binds NADP. Generally, this subgroup has poor conservation of the active site tetrad; however, individual sequences do contain matches to the YXXXK active site motif, the upstream Ser, and there is a highly conserved Asp in place of the usual active site Asn throughout the subgroup. Atypical SDRs generally lack the catalytic residues characteristic of the SDRs, and their glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif is often different from the forms normally seen in classical or extended SDRs. Atypical SDRs include biliverdin IX beta reductase (BVR-B,aka flavin reductase), NMRa (a negative transcriptional regulator of various fungi), progesterone 5-beta-reductase like proteins, phenylcoumaran benzylic ether and pinoresinol-lariciresinol reductases, phenylpropene synthases, eugenol synthase, triphenylmethane reductase, isoflavone reductases, and others. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold, an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes is typically in the 15-30% range; they catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser and/or an Asn, contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. In addition to the Rossmann fold core region typical of all SDRs, extended SDRs have a less conserved C-terminal extension of approximately 100 amino acids, and typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUU00717.1 | 6.45e-174 | 45 | 416 | 55 | 420 |
| AVM58209.1 | 8.44e-174 | 45 | 416 | 23 | 388 |
| QMI79524.1 | 8.44e-174 | 45 | 416 | 23 | 388 |
| QBJ18079.1 | 1.20e-173 | 45 | 416 | 23 | 388 |
| QPH58384.1 | 1.20e-173 | 45 | 416 | 23 | 388 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4JJA_A | 8.35e-164 | 42 | 416 | 2 | 370 | Crystalstructure of a DUF1343 family protein (BF0379) from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 at 1.30 A resolution [Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343] |
| 4K05_A | 4.01e-43 | 60 | 415 | 28 | 399 | Crystalstructure of a DUF1343 family protein (BF0371) from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 at 1.65 A resolution [Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343],4K05_B Crystal structure of a DUF1343 family protein (BF0371) from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 at 1.65 A resolution [Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P40407 | 6.39e-70 | 55 | 414 | 47 | 414 | Uncharacterized protein YbbC OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=ybbC PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
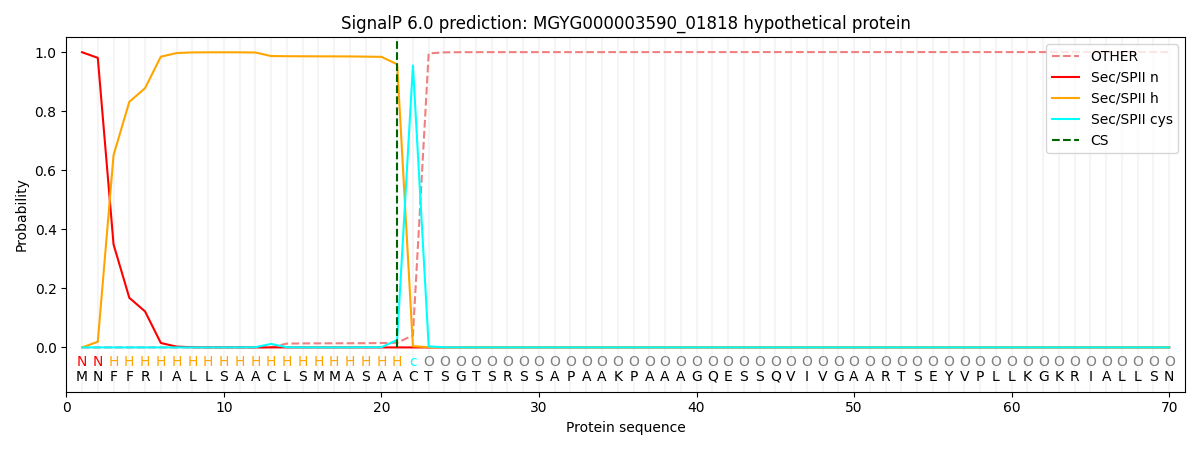
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000001 | 0.000455 | 0.999600 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
