You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003642_01952
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003642_01952
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | RUG572 sp900771305 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Verrucomicrobiota; Kiritimatiellae; RFP12; UBA1067; RUG572; RUG572 sp900771305 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003642_01952 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH97 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Retaining alpha-galactosidase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 16917; End: 18917 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH97 | 14 | 661 | 2.8e-168 | 0.9841521394611727 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam10566 | Glyco_hydro_97 | 2.22e-93 | 287 | 563 | 1 | 278 | Glycoside hydrolase 97. This domain is the catalytic region of the bacterial glycosyl-hydrolase family 97. This central part of the GH97 family protein sequences represents a typical and complete (beta/alpha)8-barrel or catalytic TIM-barrel type domain. The N- and C-terminal parts of the sequences, mainly consisting of beta-strands, form two additional non-catalytic domains. In all known glycosidases with the (beta-alpha)8-barrel fold, the amino acid residues at the active site are located on the C-termini of the beta-strands. |
| pfam14508 | GH97_N | 2.97e-62 | 24 | 281 | 1 | 235 | Glycosyl-hydrolase 97 N-terminal. This N-terminal domain of glycosyl-hydrolase-97 contributes part of the active site pocket. It is also important for contact with the catalytic and C-terminal domains of the whole. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUN33356.1 | 2.17e-123 | 1 | 666 | 2 | 659 |
| ADV26334.1 | 8.10e-122 | 11 | 660 | 18 | 653 |
| QAY76642.1 | 8.86e-122 | 11 | 662 | 14 | 654 |
| ATS61338.1 | 2.73e-119 | 9 | 665 | 15 | 654 |
| QWN17398.1 | 2.73e-119 | 9 | 665 | 15 | 654 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3A24_A | 2.64e-73 | 23 | 657 | 5 | 635 | Crystalstructure of BT1871 retaining glycosidase [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron],3A24_B Crystal structure of BT1871 retaining glycosidase [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron] |
| 5E1Q_A | 3.52e-72 | 23 | 657 | 19 | 649 | Mutant(D415G) GH97 alpha-galactosidase in complex with Gal-Lac [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],5E1Q_B Mutant (D415G) GH97 alpha-galactosidase in complex with Gal-Lac [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 5HQ4_A | 2.43e-60 | 21 | 662 | 2 | 658 | AGlycoside Hydrolase Family 97 enzyme from Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain K8 [Pseudoalteromonas sp. K8],5HQA_A A Glycoside Hydrolase Family 97 enzyme in complex with Acarbose from Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain K8 [Pseudoalteromonas sp. K8] |
| 5HQC_A | 2.43e-60 | 21 | 662 | 2 | 658 | AGlycoside Hydrolase Family 97 enzyme R171K variant from Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain K8 [Pseudoalteromonas sp. K8] |
| 5HQB_A | 6.37e-60 | 21 | 662 | 2 | 658 | AGlycoside Hydrolase Family 97 enzyme (E480Q) in complex with Panose from Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain K8 [Pseudoalteromonas sp. K8] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8A6L0 | 1.59e-73 | 21 | 657 | 24 | 656 | Retaining alpha-galactosidase OS=Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (strain ATCC 29148 / DSM 2079 / JCM 5827 / CCUG 10774 / NCTC 10582 / VPI-5482 / E50) OX=226186 GN=BT_1871 PE=1 SV=1 |
| D7CFN7 | 3.42e-68 | 37 | 661 | 57 | 619 | Probable retaining alpha-galactosidase OS=Streptomyces bingchenggensis (strain BCW-1) OX=749414 GN=SBI_01652 PE=3 SV=1 |
| G8JZS4 | 1.77e-45 | 1 | 666 | 1 | 727 | Glucan 1,4-alpha-glucosidase SusB OS=Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (strain ATCC 29148 / DSM 2079 / JCM 5827 / CCUG 10774 / NCTC 10582 / VPI-5482 / E50) OX=226186 GN=susB PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
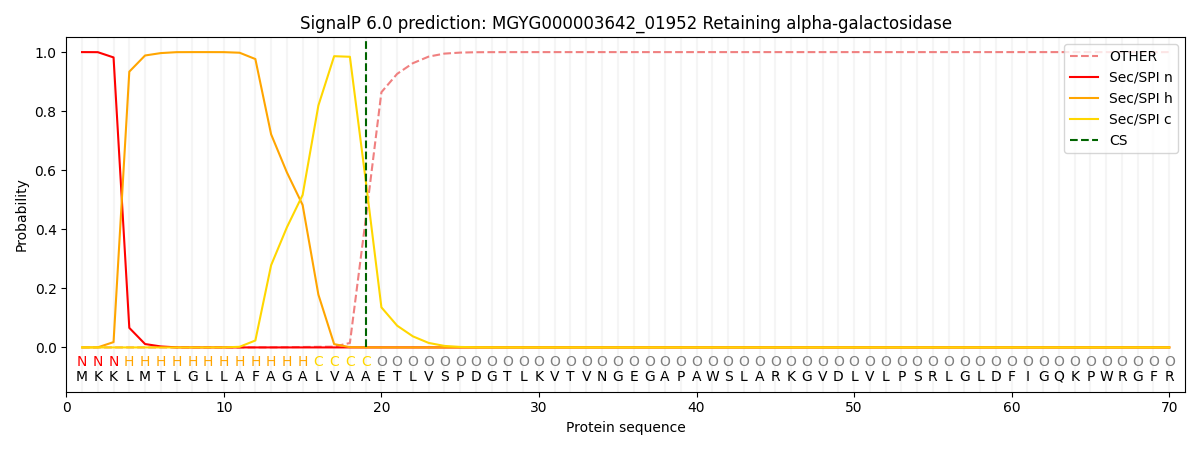
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000501 | 0.998689 | 0.000236 | 0.000193 | 0.000177 | 0.000177 |
