You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003745_00320
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003745_00320
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Actinobacteriota; Coriobacteriia; Coriobacteriales; Eggerthellaceae; CAG-1427; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003745_00320 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH25 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 123; End: 3821 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH25 | 696 | 894 | 9.1e-41 | 0.9943502824858758 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06414 | GH25_LytC-like | 5.27e-69 | 693 | 904 | 1 | 191 | The LytC lysozyme of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a bacterial cell wall hydrolase that cleaves the beta1-4-glycosydic bond located between the N-acetylmuramoyl-N-glucosaminyl residues of the cell wall polysaccharide chains. LytC is composed of a C-terminal glycosyl hydrolase family 25 (GH25) domain and an N-terminal choline-binding module (CBM) consisting of eleven homologous repeats that specifically recognizes the choline residues of pneumococcal lipoteichoic and teichoic acids. This domain arrangement is the reverse of the major pneumococcal autolysin, LytA, and the CPL-1-like lytic enzymes of the pneumococcal bacteriophages, in which the CBM (consisting of six repeats) is at the C-terminus. This model represents the C-terminal catalytic domain of the LytC-like enzymes. |
| cd07484 | Peptidases_S8_Thermitase_like | 1.51e-45 | 217 | 493 | 9 | 257 | Peptidase S8 family domain in Thermitase-like proteins. Thermitase is a non-specific, trypsin-related serine protease with a very high specific activity. It contains a subtilisin like domain. The tertiary structure of thermitase is similar to that of subtilisin BPN'. It contains a Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad. Members of the peptidases S8 (subtilisin and kexin) and S53 (sedolisin) clan include endopeptidases and exopeptidases. The S8 family has an Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad similar to that found in trypsin-like proteases, but do not share their three-dimensional structure and are not homologous to trypsin. Serine acts as a nucleophile, aspartate as an electrophile, and histidine as a base. The S53 family contains a catalytic triad Glu/Asp/Ser with an additional acidic residue Asp in the oxyanion hole, similar to that of subtilisin. The serine residue here is the nucleophilic equivalent of the serine residue in the S8 family, while glutamic acid has the same role here as the histidine base. However, the aspartic acid residue that acts as an electrophile is quite different. In S53 the it follows glutamic acid, while in S8 it precedes histidine. The stability of these enzymes may be enhanced by calcium, some members have been shown to bind up to 4 ions via binding sites with different affinity. There is a great diversity in the characteristics of their members: some contain disulfide bonds, some are intracellular while others are extracellular, some function at extreme temperatures, and others at high or low pH values. |
| cd07473 | Peptidases_S8_Subtilisin_like | 7.31e-45 | 237 | 493 | 2 | 259 | Peptidase S8 family domain in Subtilisin-like proteins. This family is a member of the Peptidases S8 or Subtilases serine endo- and exo-peptidase clan. They have an Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad similar to that found in trypsin-like proteases, but do not share their three-dimensional structure and are not homologous to trypsin. The stability of subtilases may be enhanced by calcium, some members have been shown to bind up to 4 ions via binding sites with different affinity. Some members of this clan contain disulfide bonds. These enzymes can be intra- and extracellular, some function at extreme temperatures and pH values. |
| cd07477 | Peptidases_S8_Subtilisin_subset | 6.76e-41 | 239 | 491 | 2 | 229 | Peptidase S8 family domain in Subtilisin proteins. This group is composed of many different subtilisins: Pro-TK-subtilisin, subtilisin Carlsberg, serine protease Pb92 subtilisin, and BPN subtilisins just to name a few. Pro-TK-subtilisin is a serine protease from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis and consists of a signal peptide, a propeptide, and a mature domain. TK-subtilisin is matured from pro-TK-subtilisin upon autoprocessing and degradation of the propeptide. Unlike other subtilisins though, the folding of the unprocessed form of pro-TK-subtilisin is induced by Ca2+ binding which is almost completed prior to autoprocessing. Ca2+ is required for activity unlike the bacterial subtilisins. The propeptide is not required for folding of the mature domain unlike the bacterial subtilases because of the stability produced from Ca2+ binding. Subtilisin Carlsberg is extremely similar in structure to subtilisin BPN'/Novo thought it has a 30% difference in amino acid sequence. The substrate binding regions are also similar and 2 possible Ca2+ binding sites have been identified recently. Subtilisin Carlsberg possesses the highest commercial importance as a proteolytic additive for detergents. Serine protease Pb92, the serine protease from the alkalophilic Bacillus strain PB92, also contains two calcium ions and the overall folding of the polypeptide chain closely resembles that of the subtilisins. Members of the peptidases S8 and S35 clan include endopeptidases, exopeptidases and also a tripeptidyl-peptidase. The S8 family has an Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad similar to that found in trypsin-like proteases, but do not share their three-dimensional structure and are not homologous to trypsin. The S53 family contains a catalytic triad Glu/Asp/Ser. The stability of these enzymes may be enhanced by calcium, some members have been shown to bind up to 4 ions via binding sites with different affinity. Some members of this clan contain disulfide bonds. These enzymes can be intra- and extracellular, some function at extreme temperatures and pH values. |
| cd00306 | Peptidases_S8_S53 | 3.51e-37 | 239 | 491 | 1 | 241 | Peptidase domain in the S8 and S53 families. Members of the peptidases S8 (subtilisin and kexin) and S53 (sedolisin) family include endopeptidases and exopeptidases. The S8 family has an Asp/His/Ser catalytic triad similar to that found in trypsin-like proteases, but do not share their three-dimensional structure and are not homologous to trypsin. Serine acts as a nucleophile, aspartate as an electrophile, and histidine as a base. The S53 family contains a catalytic triad Glu/Asp/Ser with an additional acidic residue Asp in the oxyanion hole, similar to that of subtilisin. The serine residue here is the nucleophilic equivalent of the serine residue in the S8 family, while glutamic acid has the same role here as the histidine base. However, the aspartic acid residue that acts as an electrophile is quite different. In S53, it follows glutamic acid, while in S8 it precedes histidine. The stability of these enzymes may be enhanced by calcium; some members have been shown to bind up to 4 ions via binding sites with different affinity. There is a great diversity in the characteristics of their members: some contain disulfide bonds, some are intracellular while others are extracellular, some function at extreme temperatures, and others at high or low pH values. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAK44097.1 | 2.32e-229 | 36 | 915 | 38 | 834 |
| BCA89043.1 | 4.91e-66 | 629 | 905 | 160 | 417 |
| BCS56855.1 | 3.64e-49 | 628 | 905 | 156 | 441 |
| AEB07228.1 | 7.96e-49 | 629 | 904 | 67 | 320 |
| QUF79171.1 | 1.97e-48 | 688 | 893 | 75 | 259 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3QTL_A | 2.84e-25 | 231 | 492 | 14 | 253 | StructuralBasis for Dual-inhibition Mechanism of a Non-classical Kazal-type Serine Protease Inhibitor from Horseshoe Crab in Complex with Subtilisin [Bacillus licheniformis],3QTL_B Structural Basis for Dual-inhibition Mechanism of a Non-classical Kazal-type Serine Protease Inhibitor from Horseshoe Crab in Complex with Subtilisin [Bacillus licheniformis],3QTL_C Structural Basis for Dual-inhibition Mechanism of a Non-classical Kazal-type Serine Protease Inhibitor from Horseshoe Crab in Complex with Subtilisin [Bacillus licheniformis],4HX2_A Crystal structure of Streptomyces caespitosus sermetstatin in complex with Bacillus licheniformis subtilisin [Bacillus licheniformis],4HX2_C Crystal structure of Streptomyces caespitosus sermetstatin in complex with Bacillus licheniformis subtilisin [Bacillus licheniformis] |
| 1C3L_A | 2.84e-25 | 231 | 492 | 14 | 253 | Subtilisin-CarlsbergComplexed With Xenon (8 Bar) [Bacillus licheniformis],3UNX_A Bond length analysis of asp, glu and his residues in subtilisin Carlsberg at 1.26A resolution [Bacillus licheniformis] |
| 4GI3_A | 2.91e-25 | 231 | 492 | 15 | 254 | Crystalstructure of Greglin in complex with subtilisin [Bacillus licheniformis] |
| 1AF4_A | 7.08e-25 | 231 | 492 | 14 | 253 | CRYSTALSTRUCTURE OF SUBTILISIN CARLSBERG IN ANHYDROUS DIOXANE [Bacillus licheniformis],1BE6_A TRANS-CINNAMOYL-SUBTILISIN IN ANHYDROUS ACETONITRILE [Bacillus licheniformis],1BE8_A TRANS-CINNAMOYL-SUBTILISIN IN WATER [Bacillus licheniformis],1BFK_A Crystal Structure Of Subtilisin Carlsberg In 40% Acetonitrile [Bacillus licheniformis],1BFU_A SUBTILISIN CARLSBERG IN 20% DIOXANE [Bacillus licheniformis],1CSE_E THE HIGH-RESOLUTION X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX FORMED BETWEEN SUBTILISIN CARLSBERG AND EGLIN C, AN ELASTASE INHIBITOR FROM THE LEECH HIRUDO MEDICINALIS. STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS, SUBTILISIN STRUCTURE AND INTERFACE GEOMETRY [Bacillus subtilis],1OYV_A Chain A, Subtilisin Carlsberg [Bacillus licheniformis],1OYV_B Chain B, Subtilisin Carlsberg [Bacillus licheniformis],1R0R_E 1.1 Angstrom Resolution Structure of the Complex Between the Protein Inhibitor, OMTKY3, and the Serine Protease, Subtilisin Carlsberg [Bacillus licheniformis],1SBC_A The Refined Crystal Structure Of Subtilisin Carlsberg At 2.5 Angstroms Resolution [Bacillus subtilis],1SCA_A ENZYME CRYSTAL STRUCTURE IN A NEAT ORGANIC SOLVENT [Bacillus licheniformis],1SCB_A ENZYME CRYSTAL STRUCTURE IN A NEAT ORGANIC SOLVENT [Bacillus licheniformis],1SCD_A X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CROSS-LINKED SUBTILISM CARLSBERG IN WATER VS. ACETONITRILE [Bacillus licheniformis],2SEC_E STRUCTURAL COMPARISON OF TWO SERINE PROTEINASE-PROTEIN INHIBITOR COMPLEXES. EGLIN-C-SUBTILISIN CARLSBERG AND CI-2-SUBTILISIN NOVO [Bacillus licheniformis],2WUV_A Crystallographic analysis of counter-ion effects on subtilisin enzymatic action in acetonitrile [Bacillus licheniformis],2WUW_E Crystallographic analysis of counter-ion effects on subtilisin enzymatic action in acetonitrile (native data) [Bacillus licheniformis],4C3U_A Extensive counter-ion interactions with subtilisin in aqueous medium, Cs derivative [Bacillus licheniformis],4C3V_A Extensive counter-ion interactions with subtilisin in aqueous medium, no Cs soak [Bacillus licheniformis] |
| 1YU6_A | 7.24e-25 | 231 | 492 | 15 | 254 | CrystalStructure of the Subtilisin Carlsberg:OMTKY3 Complex [Bacillus licheniformis],1YU6_B Crystal Structure of the Subtilisin Carlsberg:OMTKY3 Complex [Bacillus licheniformis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q45670 | 2.58e-24 | 173 | 497 | 95 | 383 | Thermophilic serine proteinase OS=Bacillus sp. (strain AK1) OX=268807 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P00780 | 1.48e-23 | 231 | 492 | 119 | 358 | Subtilisin Carlsberg OS=Bacillus licheniformis OX=1402 GN=subC PE=1 SV=2 |
| P00781 | 1.09e-22 | 231 | 492 | 14 | 253 | Subtilisin DY OS=Bacillus licheniformis OX=1402 GN=apr PE=1 SV=1 |
| P04072 | 7.49e-22 | 229 | 497 | 23 | 261 | Thermitase OS=Thermoactinomyces vulgaris OX=2026 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P54423 | 2.63e-20 | 241 | 503 | 458 | 694 | Cell wall-associated protease OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=wprA PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
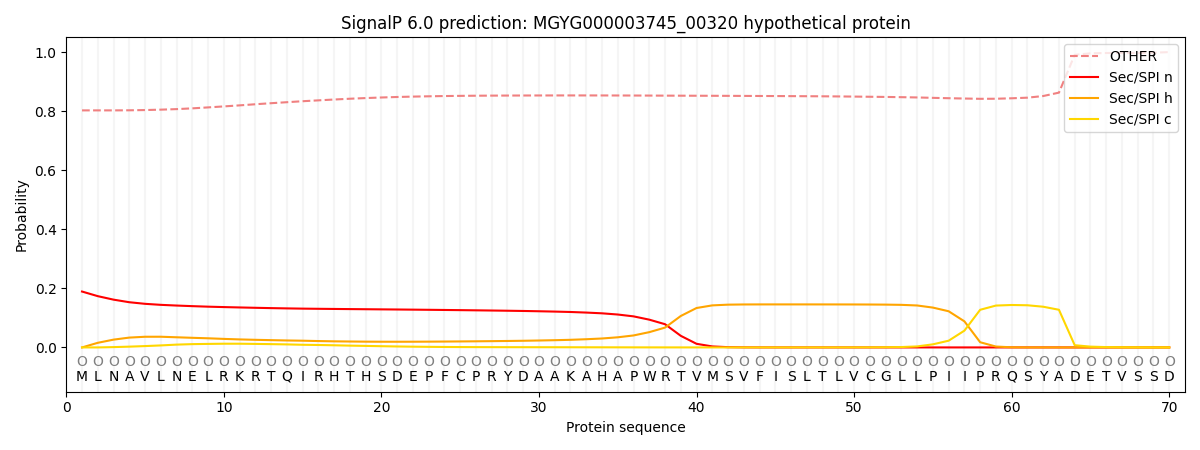
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.810127 | 0.173044 | 0.012714 | 0.002930 | 0.000480 | 0.000687 |
