You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003919_00455
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003919_00455
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
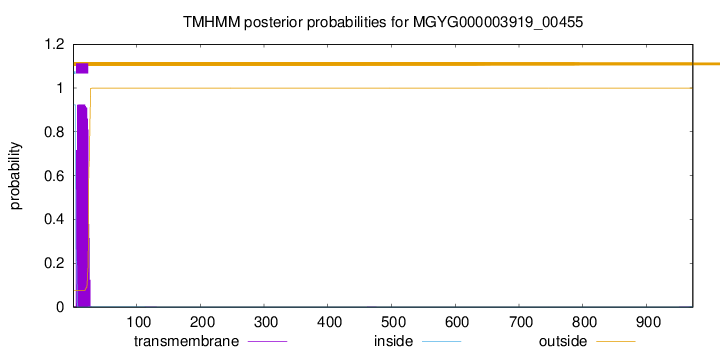
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Fusobacterium_A sp900555845 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Fusobacteriota; Fusobacteriia; Fusobacteriales; Fusobacteriaceae; Fusobacterium_A; Fusobacterium_A sp900555845 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003919_00455 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | PL8 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Chondroitin sulfate ABC exolyase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 13057; End: 15978 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL8 | 578 | 812 | 1.3e-80 | 0.9919028340080972 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd01083 | GAG_Lyase | 3.25e-105 | 243 | 889 | 25 | 693 | Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) polysaccharide lyase family. This family consists of a group of secreted bacterial lyase enzymes capable of acting on glycosaminoglycans, such as hyaluronan and chondroitin, in the extracellular matrix of host tissues, contributing to the invasive capacity of the pathogen. These are broad-specificity glycosaminoglycan lyases which recognize uronyl residues in polysaccharides and cleave their glycosidic bonds via a beta-elimination reaction to form a double bond between C-4 and C-5 of the non-reducing terminal uronyl residues of released products. Substrates include chondroitin, chondroitin 4-sulfate, chondroitin 6-sulfate, and hyaluronic acid. Family members include chondroitin AC lyase, chondroitin abc lyase, xanthan lyase, and hyalurate lyase. |
| pfam09093 | Lyase_catalyt | 8.48e-72 | 214 | 545 | 6 | 356 | Lyase, catalytic. Members of this family are predominantly found in chondroitin ABC lyase I, and adopt a helical structure, with fifteen alpha-helices which are at least two turns long and several short helical turns. The bulk of the domain is formed by ten alpha-helices forming five hairpin-like pairs and arranged into an incomplete toroid, the (alpha/alpha)5 fold. Additionally, two long and two short alpha-helices at the N-terminus of the domain wrap around the toroid. At the C-terminal end of the toroid there is one additional short alpha-helix. This domain is required for degradation of polysaccharides containing 1,4-beta-D-hexosaminyl and 1,3-beta-D-glucoronosyl or 1,3-alpha-L-iduronosyl linkages to disaccharides containing 4-deoxy-beta-D-gluc-4-enuronosyl groups. |
| pfam09092 | Lyase_N | 3.16e-48 | 23 | 183 | 4 | 167 | Lyase, N terminal. Members of this family are predominantly found in chondroitin ABC lyase I, and adopt a jelly-roll fold topology consisting of a two-layered bent beta-sheet sandwich with one short alpha-helix. The convex beta sheet is composed of five antiparallel strands, whilst the concave beta-sheet contains five antiparallel beta-strands with a loop between two consecutive strands folding back onto the concave surface. This domain is required for binding of the protein to long glycosaminoglycan chains. |
| pfam02278 | Lyase_8 | 1.04e-26 | 577 | 812 | 11 | 248 | Polysaccharide lyase family 8, super-sandwich domain. This family consists of a group of secreted bacterial lyase enzymes EC:4.2.2.1 capable of acting on hyaluronan and chondroitin in the extracellular matrix of host tissues, contributing to the invasive capacity of the pathogen. |
| cd03857 | M14-like | 0.005 | 168 | 234 | 42 | 105 | Peptidase M14-like domain; uncharacterized subfamily. Peptidase M14-like domain of a functionally uncharacterized subgroup of the M14 family of metallocarboxypeptidases (MCPs). The M14 family are zinc-binding carboxypeptidases (CPs) which hydrolyze single, C-terminal amino acids from polypeptide chains, and have a recognition site for the free C-terminal carboxyl group, which is a key determinant of specificity. Two major subfamilies of the M14 family, defined based on sequence and structural homology, are the A/B and N/E subfamilies. Enzymes belonging to the A/B subfamily are normally synthesized as inactive precursors containing preceding signal peptide, followed by an N-terminal pro-region linked to the enzyme; these proenzymes are called procarboxypeptidases. The A/B enzymes can be further divided based on their substrate specificity; Carboxypeptidase A-like (CPA-like) enzymes favor hydrophobic residues while carboxypeptidase B-like (CPB-like) enzymes only cleave the basic residues lysine or arginine. The A forms have slightly different specificities, with Carboxypeptidase A1 (CPA1) preferring aliphatic and small aromatic residues, and CPA2 preferring the bulky aromatic side chains. Enzymes belonging to the N/E subfamily enzymes are not produced as inactive precursors and instead rely on their substrate specificity and subcellular compartmentalization to prevent inappropriate cleavage. They contain an extra C-terminal transthyretin-like domain, thought to be involved in folding or formation of oligomers. MCPs can also be classified based on their involvement in specific physiological processes; the pancreatic MCPs participate only in alimentary digestion and include carboxypeptidase A and B (A/B subfamily), while others, namely regulatory MCPs or the N/E subfamily, are involved in more selective reactions, mainly in non-digestive tissues and fluids, acting on blood coagulation/fibrinolysis, inflammation and local anaphylaxis, pro-hormone and neuropeptide processing, cellular response and others. Another MCP subfamily, is that of succinylglutamate desuccinylase /aspartoacylase, which hydrolyzes N-acetyl-L-aspartate (NAA), and deficiency in which is the established cause of Canavan disease. Another subfamily (referred to as subfamily C) includes an exceptional type of activity in the MCP family, that of dipeptidyl-peptidase activity of gamma-glutamyl-(L)-meso-diaminopimelate peptidase I which is involved in bacterial cell wall metabolism. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVQ18406.1 | 0.0 | 8 | 973 | 18 | 982 |
| QNM15141.1 | 0.0 | 10 | 972 | 11 | 973 |
| QUH29903.1 | 7.35e-245 | 23 | 947 | 216 | 1187 |
| APC49583.1 | 6.67e-226 | 24 | 970 | 202 | 1179 |
| QZE14915.1 | 2.63e-204 | 39 | 954 | 42 | 1000 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2Q1F_A | 4.40e-164 | 24 | 938 | 23 | 980 | Crystalstructure of chondroitin sulfate lyase abc from bacteroides thetaiotaomicron wal2926 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron],2Q1F_B Crystal structure of chondroitin sulfate lyase abc from bacteroides thetaiotaomicron wal2926 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron] |
| 1HN0_A | 3.10e-93 | 23 | 973 | 41 | 1020 | CRYSTALSTRUCTURE OF CHONDROITIN ABC LYASE I FROM PROTEUS VULGARIS AT 1.9 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION [Proteus vulgaris] |
| 7EIP_A | 4.26e-93 | 23 | 973 | 41 | 1020 | ChainA, Chondroitin sulfate ABC endolyase [Proteus vulgaris],7EIQ_A Chain A, Chondroitin sulfate ABC endolyase [Proteus vulgaris],7EIR_A Chain A, Chondroitin sulfate ABC endolyase [Proteus vulgaris],7EIS_A Chain A, Chondroitin sulfate ABC endolyase [Proteus vulgaris] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7S340 | 6.21e-179 | 23 | 938 | 12 | 956 | Chondroitin sulfate ABC exolyase (Fragment) OS=Proteus vulgaris OX=585 GN=ChABCII PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q8A2I1 | 5.44e-172 | 23 | 938 | 22 | 980 | Chondroitin sulfate ABC exolyase OS=Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (strain ATCC 29148 / DSM 2079 / JCM 5827 / CCUG 10774 / NCTC 10582 / VPI-5482 / E50) OX=226186 GN=chonabc PE=1 SV=1 |
| C5G6D7 | 7.64e-172 | 23 | 938 | 22 | 980 | Chondroitin sulfate ABC exolyase OS=Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron OX=818 GN=chonabc PE=1 SV=2 |
| P59807 | 2.33e-92 | 23 | 973 | 41 | 1020 | Chondroitin sulfate ABC endolyase OS=Proteus vulgaris OX=585 PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
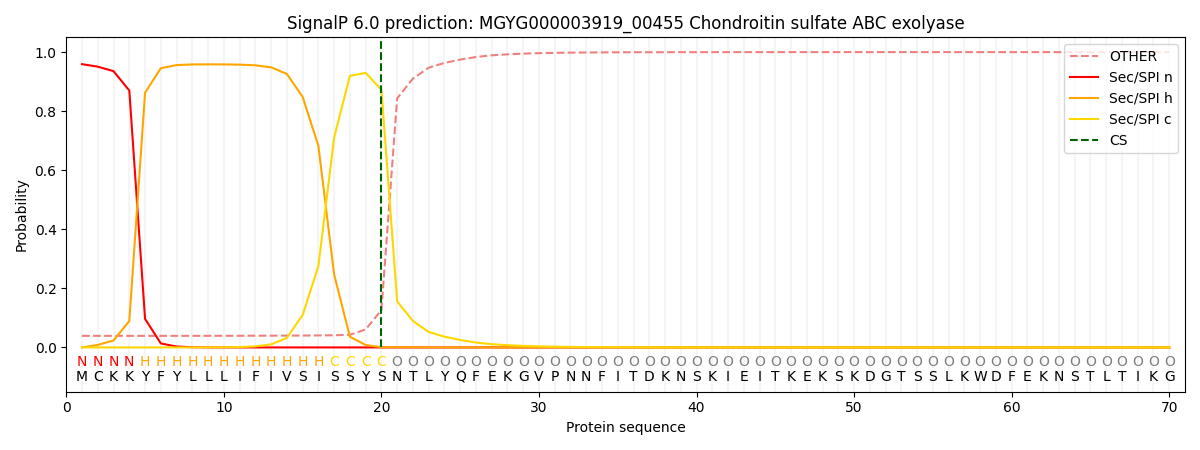
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.044103 | 0.952629 | 0.002321 | 0.000343 | 0.000280 | 0.000297 |