You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003926_01022
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003926_01022
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
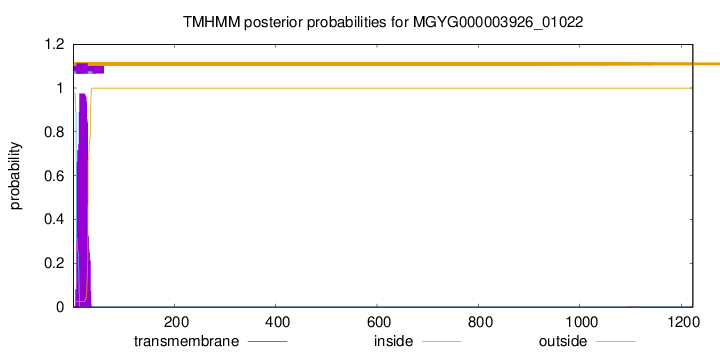
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Rikenella microfusus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Rikenella; Rikenella microfusus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003926_01022 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM51 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 2552; End: 6223 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam18582 | HZS_alpha | 2.23e-48 | 772 | 863 | 1 | 98 | Hydrazine synthase alpha subunit middle domain. The crystal structure of hydrazine synthase multiprotein complex isolated from the anammox organism Kuenenia stuttgartiensis implies a two-step mechanism for hydrazine synthesis: a three-electron reduction of nitric oxide to hydroxylamine at the active site of the gamma-subunit and its subsequent condensation with ammonia, yielding hydrazine in the active centre of the alpha-subunit. The alpha-subunit consists of three domains: an N-terminal domain which includes a six-bladed beta-propeller, a middle domain binding a pentacoordinated c-type haem (haem alphaI) and a C-terminal domain which harbours a bis-histidine-coordinated c-type haem (haem alphaII). This entry represents the middle domain of subunit alpha of hydrazine synthase (HZS). |
| pfam03781 | FGE-sulfatase | 1.57e-22 | 1105 | 1220 | 5 | 134 | Sulfatase-modifying factor enzyme 1. This domain is found in eukaryotic proteins required for post-translational sulfatase modification (SUMF1). These proteins are associated with the rare disorder multiple sulfatase deficiency (MSD). The protein product of the SUMF1 gene is FGE, formylglycine (FGly),-generating enzyme, which is a sulfatase. Sulfatases are enzymes essential for degradation and remodelling of sulfate esters, and formylglycine (FGly), the key catalytic in the active site, is unique to sulfatases. FGE is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and interacts with and modifies the unfolded form of newly synthesized sulfatases. FGE is a single-domain monomer with a surprising paucity of secondary structure that adopts a unique fold which is stabilized by two Ca2+ ions. The effect of all mutations found in MSD patients is explained by the FGE structure, providing a molecular basis for MSD. A redox-active disulfide bond is present in the active site of FGE. An oxidized cysteine residue, possibly cysteine sulfenic acid, has been detected that may allow formulation of a structure-based mechanism for FGly formation from cysteine residues in all sulfatases. In Mycobacteria and Treponema denticola this enzyme functions as an iron(II)-dependent oxidoreductase. |
| COG1262 | YfmG | 3.81e-19 | 1099 | 1223 | 47 | 181 | Formylglycine-generating enzyme, required for sulfatase activity, contains SUMF1/FGE domain [Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones]. |
| pfam08305 | NPCBM | 8.37e-17 | 136 | 217 | 1 | 82 | NPCBM/NEW2 domain. This novel putative carbohydrate binding module (NPCBM) domain is found at the N-terminus of glycosyl hydrolase family 98 proteins. This domain has also been called the NEW2 domain (Naumoff DG. Phylogenetic analysis of alpha-galactosidases of the GH27 family. Molecular Biology (Engl Transl). (2004)38:388-399.) |
| smart00776 | NPCBM | 3.62e-10 | 138 | 222 | 5 | 96 | This novel putative carbohydrate binding module (NPCBM) domain is found at the N-terminus of glycosyl hydrolase family 98 proteins. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUT74006.1 | 0.0 | 33 | 1223 | 20 | 1189 |
| ASV76038.1 | 1.23e-59 | 319 | 1009 | 214 | 920 |
| AQT69174.1 | 2.07e-57 | 455 | 1019 | 238 | 777 |
| ARN56721.1 | 2.32e-17 | 1085 | 1218 | 24 | 150 |
| QDU19822.1 | 5.23e-15 | 1101 | 1218 | 31 | 152 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6S07_A | 8.97e-06 | 1096 | 1219 | 16 | 170 | Structureof formylglycine-generating enzyme at 1.04 A in complex with copper and substrate reveals an acidic pocket for binding and acti-vation of molecular oxygen. [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183],6XTL_A Chain A, Formylglycine-generating enzyme [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183],6XTM_A Chain A, Formylglycine-generating enzyme [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183],6XTN_A Chain A, Formylglycine-generating enzyme [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183],6XTO_A Chain A, Formylglycine-generating enzyme [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183],6XTP_A Chain A, Formylglycine-generating enzyme [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183],6XTQ_A Chain A, Formylglycine-generating enzyme [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183],6XTR_A Chain A, Formylglycine-generating enzyme [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183],6XTS_A Chain A, Formylglycine-generating enzyme [Thermomonospora curvata DSM 43183] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q58CP2 | 2.79e-06 | 1095 | 1220 | 20 | 179 | Inactive C-alpha-formylglycine-generating enzyme 2 OS=Bos taurus OX=9913 GN=SUMF2 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
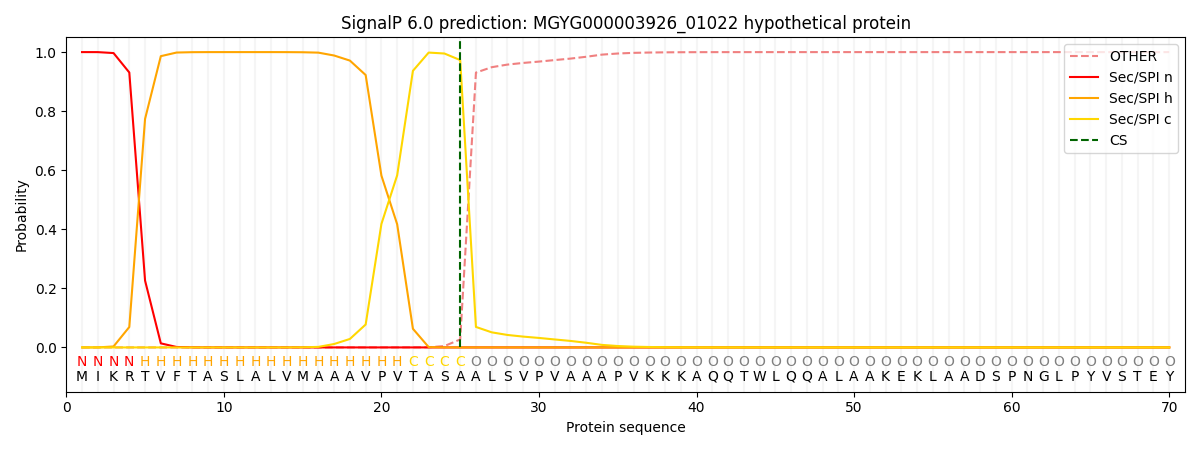
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000377 | 0.998733 | 0.000222 | 0.000245 | 0.000208 | 0.000183 |