You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004067_00116
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004067_00116
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; CAG-274; ; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004067_00116 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM77 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 34645; End: 37122 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBM77 | 492 | 597 | 4.8e-35 | 0.9805825242718447 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam18283 | CBM77 | 1.42e-37 | 489 | 599 | 1 | 108 | Carbohydrate binding module 77. This domain is the non-catalytic carbohydrate binding module 77 (CBM77) present in Ruminococcus flavefaciens. CBMs fulfil a critical targeting function in plant cell wall depolymerisation. In CBM77, a cluster of conserved basic residues (Lys1092, Lys1107 and Lys1162) confer calcium-independent recognition of homogalacturonan. |
| cd14256 | Dockerin_I | 8.03e-11 | 641 | 694 | 2 | 54 | Type I dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. The cellulosome consists of scaffoldin, a noncatalytic scaffolding polypeptide, that comprises repeating cohesion modules and a single carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). Specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesins and dockerins appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly. This subfamily represents type I dockerins, which are responsible for anchoring a variety of enzymatic domains to the complex. |
| cd14254 | Dockerin_II | 8.53e-07 | 641 | 695 | 1 | 52 | Type II dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. The cellulosome consists of scaffoldin, a noncatalytic scaffolding polypeptide, that comprises repeating cohesion modules and a single carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). Specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesins and dockerins appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly. This subfamily represents type II dockerins, which are responsible for mediating attachment of the cellulosome complex to the bacterial cell wall. |
| pfam00404 | Dockerin_1 | 3.32e-06 | 641 | 696 | 1 | 54 | Dockerin type I repeat. The dockerin repeat is the binding partner of the cohesin domain pfam00963. The cohesin-dockerin interaction is the crucial interaction for complex formation in the cellulosome. The dockerin repeats, each bearing homology to the EF-hand calcium-binding loop bind calcium. |
| cd14253 | Dockerin | 6.66e-04 | 641 | 695 | 1 | 54 | Dockerin repeat domain. Dockerins are modules in the cellulosome complex that often anchor catalytic subunits by binding to cohesin domains of scaffolding proteins. Three types of dockerins and their corresponding cohesin have been described in the literature. This alignment models two consecutive dockerin repeats, the functional unit. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QEH67539.1 | 7.74e-149 | 43 | 463 | 35 | 450 |
| CDM68951.1 | 2.02e-97 | 48 | 461 | 44 | 449 |
| ACR71161.1 | 3.12e-24 | 489 | 611 | 779 | 902 |
| QQY82326.1 | 8.80e-21 | 442 | 609 | 600 | 756 |
| AIQ38798.1 | 9.45e-21 | 488 | 599 | 603 | 709 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5FU5_A | 4.89e-25 | 487 | 602 | 4 | 114 | Thecomplexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens cellulosome reflects an expansion in glycan recognition [Ruminococcus flavefaciens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
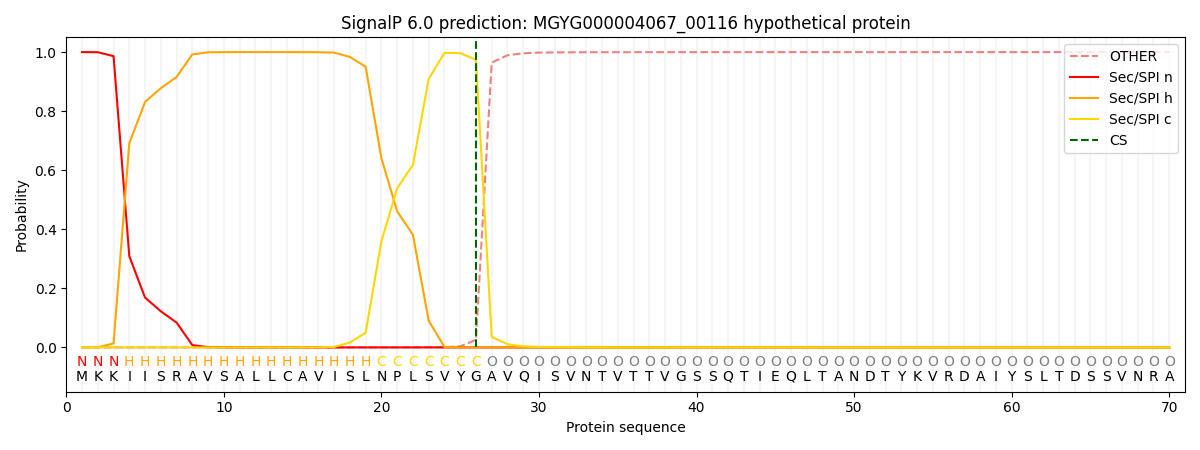
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000259 | 0.999102 | 0.000192 | 0.000154 | 0.000146 | 0.000138 |
