You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004325_00304
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004325_00304
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
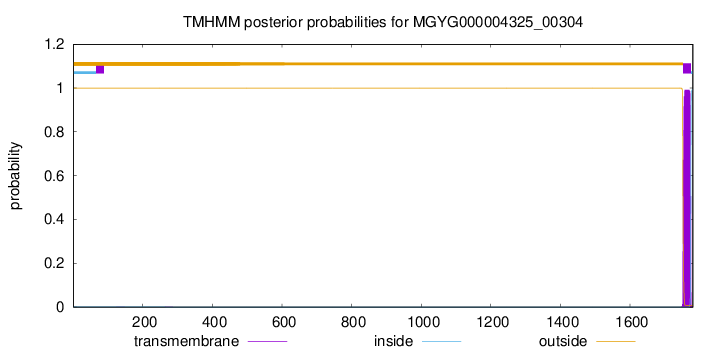
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Actinobacteriota; Coriobacteriia; Coriobacteriales; Coriobacteriaceae; Collinsella; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004325_00304 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH31 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 30500; End: 35845 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH31 | 135 | 388 | 1.2e-49 | 0.5386416861826698 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06596 | GH31_CPE1046 | 8.61e-138 | 9 | 359 | 43 | 334 | Clostridium CPE1046-like. CPE1046 is an uncharacterized Clostridium perfringens protein with a glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31) domain. The domain architecture of CPE1046 and its orthologs includes a C-terminal fibronectin type 3 (FN3) domain and a coagulation factor 5/8 type C domain in addition to the GH31 domain. Enzymes of the GH31 family possess a wide range of different hydrolytic activities including alpha-glucosidase (glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase), alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, 3-alpha-isomaltosyltransferase and alpha-1,4-glucan lyase. All GH31 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. |
| COG1501 | YicI | 9.51e-50 | 72 | 461 | 395 | 736 | Alpha-glucosidase, glycosyl hydrolase family GH31 [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| pfam01055 | Glyco_hydro_31 | 4.04e-47 | 72 | 388 | 159 | 442 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 31. Glycosyl hydrolases are key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism. Family 31 comprises of enzymes that are, or similar to, alpha- galactosidases. |
| cd08759 | Type_III_cohesin_like | 2.16e-36 | 915 | 1082 | 1 | 167 | Cohesin domain, interaction partner of dockerin. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. Two specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesin and dockerin appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly, type I and type II. This subfamily represents type III cohesins and closely related domains. |
| cd06589 | GH31 | 2.68e-36 | 7 | 258 | 21 | 265 | glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31). GH31 enzymes occur in prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea with a wide range of hydrolytic activities, including alpha-glucosidase (glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase), alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, 3-alpha-isomaltosyltransferase and alpha-1,4-glucan lyase. All GH31 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. In most cases, the pyranose moiety recognized in subsite -1 of the substrate binding site is an alpha-D-glucose, though some GH31 family members show a preference for alpha-D-xylose. Several GH31 enzymes can accommodate both glucose and xylose and different levels of discrimination between the two have been observed. Most characterized GH31 enzymes are alpha-glucosidases. In mammals, GH31 members with alpha-glucosidase activity are implicated in at least three distinct biological processes. The lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) is essential for glycogen degradation and a deficiency or malfunction of this enzyme causes glycogen storage disease II, also known as Pompe disease. In the endoplasmic reticulum, alpha-glucosidase II catalyzes the second step in the N-linked oligosaccharide processing pathway that constitutes part of the quality control system for glycoprotein folding and maturation. The intestinal enzymes sucrase-isomaltase (SI) and maltase-glucoamylase (MGAM) play key roles in the final stage of carbohydrate digestion, making alpha-glucosidase inhibitors useful in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. GH31 alpha-glycosidases are retaining enzymes that cleave their substrates via an acid/base-catalyzed, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. Two aspartic acid residues have been identified as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, respectively. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QWT17625.1 | 0.0 | 6 | 1716 | 378 | 2114 |
| QNM10857.1 | 0.0 | 5 | 1709 | 359 | 2018 |
| BCT46261.1 | 0.0 | 9 | 1704 | 376 | 2041 |
| BBK61154.1 | 0.0 | 2 | 1710 | 368 | 2075 |
| QUO30799.1 | 0.0 | 9 | 1037 | 352 | 1367 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6M76_A | 3.02e-155 | 9 | 698 | 339 | 963 | GH31alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase from Enterococcus faecalis [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100],6M77_A GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase from Enterococcus faecalis in complex with N-acetylgalactosamine [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
| 7F7R_A | 1.53e-154 | 9 | 698 | 339 | 963 | ChainA, GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
| 7F7Q_A | 4.06e-154 | 9 | 698 | 339 | 963 | ChainA, GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
| 4LPL_A | 5.29e-21 | 677 | 832 | 23 | 182 | Structureof CBM32-1 from a family 31 glycoside hydrolase from Clostridium perfringens [Clostridium perfringens ATCC 13124] |
| 7KMP_A | 8.97e-19 | 151 | 433 | 636 | 901 | ChainA, Alpha-xylosidase [Xanthomonas citri pv. citri str. 306],7KNC_A Chain A, Alpha-xylosidase [Xanthomonas citri pv. citri str. 306] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9P999 | 8.90e-24 | 128 | 437 | 376 | 662 | Alpha-xylosidase OS=Saccharolobus solfataricus (strain ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2) OX=273057 GN=xylS PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q9F234 | 8.73e-20 | 152 | 436 | 461 | 714 | Alpha-glucosidase 2 OS=Bacillus thermoamyloliquefaciens OX=1425 PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q9FN05 | 9.10e-19 | 77 | 389 | 497 | 780 | Probable glucan 1,3-alpha-glucosidase OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=PSL5 PE=1 SV=1 |
| B9F676 | 2.70e-18 | 141 | 389 | 551 | 778 | Probable glucan 1,3-alpha-glucosidase OS=Oryza sativa subsp. japonica OX=39947 GN=Os03g0216600 PE=3 SV=1 |
| A7LXT0 | 4.85e-16 | 151 | 433 | 605 | 879 | Alpha-xylosidase BoGH31A OS=Bacteroides ovatus (strain ATCC 8483 / DSM 1896 / JCM 5824 / BCRC 10623 / CCUG 4943 / NCTC 11153) OX=411476 GN=BACOVA_02646 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
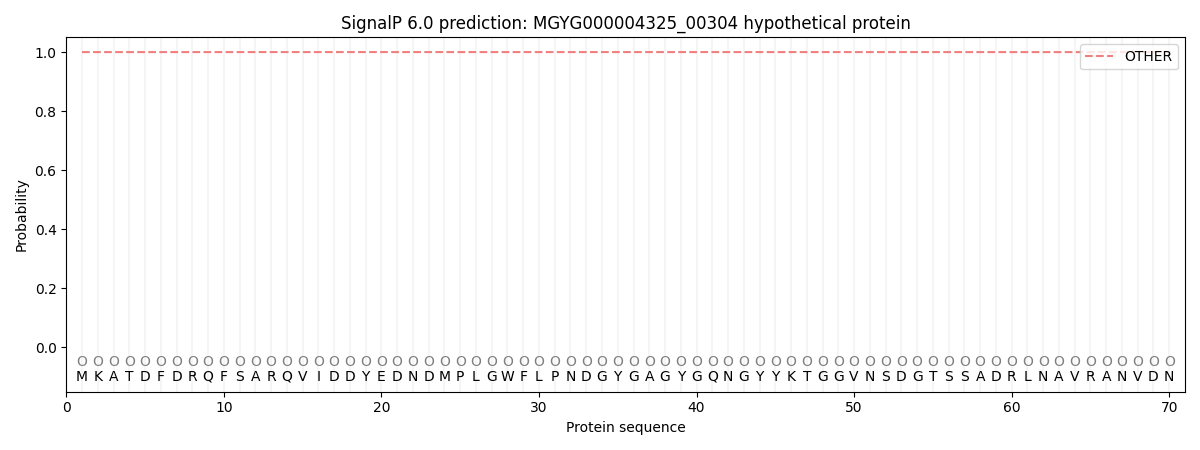
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000081 | 0.000001 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |