You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004536_01589
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004536_01589
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Alistipes sp900542505 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Alistipes; Alistipes sp900542505 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004536_01589 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH18 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 38702; End: 39829 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH18 | 46 | 326 | 9.8e-16 | 0.6081081081081081 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam16141 | DUF4849 | 3.04e-75 | 25 | 369 | 1 | 318 | Putative glycoside hydrolase Family 18, chitinase_18. This DUF is likely to be a form of glycosyl hydrolase from CAZy family 18, possibly chitinase 18. This would have the EC number of EC:3.2.1.14. |
| cd06542 | GH18_EndoS-like | 5.11e-50 | 54 | 354 | 2 | 245 | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases are bacterial chitinases that hydrolyze the chitin core of various asparagine (N)-linked glycans and glycoproteins. The endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases have a glycosyl hydrolase family 18 (GH18) catalytic domain. Some members also have an additional C-terminal glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) domain while others have an N-terminal domain of unknown function (pfam08522). Members of this family include endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase S (EndoS) from Streptococcus pyogenes, EndoF1, EndoF2, EndoF3, and EndoH from Flavobacterium meningosepticum, and EndoE from Enterococcus faecalis. EndoS is a secreted endoglycosidase from Streptococcus pyogenes that specifically hydrolyzes the glycan on human IgG between two core N-acetylglucosamine residues. EndoE is a secreted endoglycosidase, encoded by the ndoE gene in Enterococcus faecalis, that hydrolyzes the glycan on human RNase B. |
| cd00598 | GH18_chitinase-like | 1.77e-06 | 168 | 262 | 94 | 176 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of beta-1,4-linked N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) which is a major component of the cell wall of fungi and the exoskeleton of arthropods. Chitinases have been identified in viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoan parasites, insects, and plants. The structure of the GH18 domain is an eight-stranded beta/alpha barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. The GH18 family includes chitotriosidase, chitobiase, hevamine, zymocin-alpha, narbonin, SI-CLP (stabilin-1 interacting chitinase-like protein), IDGF (imaginal disc growth factor), CFLE (cortical fragment-lytic enzyme) spore hydrolase, the type III and type V plant chitinases, the endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases, and the chitolectins. The GH85 (glycosyl hydrolase, family 85) ENGases (endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases) are closely related to the GH18 chitinases and are included in this alignment model. |
| cd06548 | GH18_chitinase | 8.19e-04 | 168 | 262 | 115 | 209 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolases, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of N-acetylglucosamine and have been identified in bacteria, fungi, insects, plants, viruses, and protozoan parasites. The structure of this domain is an eight-stranded alpha/beta barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. |
| cd02878 | GH18_zymocin_alpha | 0.002 | 168 | 228 | 97 | 149 | Zymocin, alpha subunit. Zymocin is a heterotrimeric enzyme that inhibits yeast cell cycle progression. The zymocin alpha subunit has a chitinase activity that is essential for holoenzyme action from the cell exterior while the gamma subunit contains the intracellular toxin responsible for G1 phase cell cycle arrest. The zymocin alpha and beta subunits are thought to act from the cell's exterior by docking to the cell wall-associated chitin, thus mediating gamma-toxin translocation. The alpha subunit has an eight-stranded TIM barrel fold similar to that of family 18 glycosyl hydrolases such as hevamine, chitolectin, and chitobiase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUI49102.1 | 1.46e-125 | 1 | 375 | 1 | 350 |
| QCQ54233.1 | 4.15e-125 | 1 | 375 | 1 | 350 |
| QTO27699.1 | 4.15e-125 | 1 | 375 | 1 | 350 |
| QKH84627.1 | 4.15e-125 | 1 | 375 | 1 | 350 |
| QCQ32084.1 | 4.15e-125 | 1 | 375 | 1 | 350 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6Q64_A | 1.04e-49 | 4 | 366 | 2 | 351 | BT1044SeMetE190Q [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron] |
| 6KPL_A | 4.18e-08 | 42 | 372 | 19 | 297 | CrystalStructure of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Cordyceps militaris in apo form [Cordyceps militaris CM01],6KPM_A Crystal Structure of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Cordyceps militaris in complex with L-fucose [Cordyceps militaris CM01] |
| 6KPN_A | 4.26e-07 | 42 | 372 | 19 | 297 | CrystalStructure of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Cordyceps militaris D154N/E156Q mutant in complex with fucosyl-N-acetylglucosamine [Cordyceps militaris CM01],6KPO_A Crystal Structure of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Cordyceps militaris D154N/E156Q mutant in complex with fucosyl-N-acetylglucosamine-Asn [Cordyceps militaris CM01] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P36912 | 1.97e-08 | 47 | 372 | 55 | 335 | Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F2 OS=Elizabethkingia meningoseptica OX=238 GN=endOF2 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
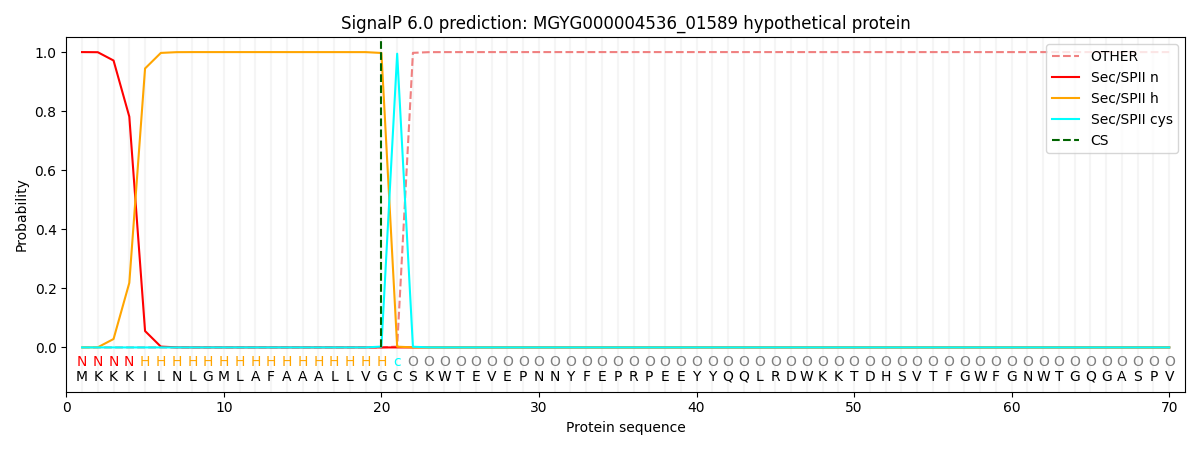
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000026 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
