You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004609_01716
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004609_01716
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
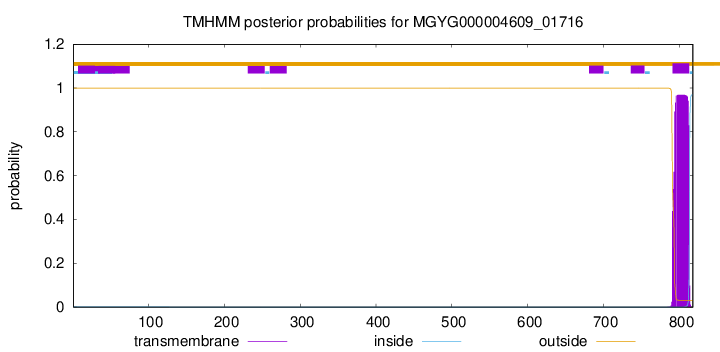
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Mediterraneibacter; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004609_01716 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH146 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 231; End: 2687 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH146 | 2 | 535 | 4.2e-181 | 0.9701789264413518 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam07944 | Glyco_hydro_127 | 3.72e-138 | 1 | 534 | 13 | 501 | Beta-L-arabinofuranosidase, GH127. One member of this family, from Bidobacterium longicum, UniProtKB:E8MGH8, has been characterized as an unusual beta-L-arabinofuranosidase enzyme, EC:3.2.1.185. It rleases l-arabinose from the l-arabinofuranose (Araf)-beta1,2-Araf disaccharide and also transglycosylates 1-alkanols with retention of the anomeric configuration. Terminal beta-l-arabinofuranosyl residues have been found in arabinogalactan proteins from a mumber of different plantt species. beta-l-Arabinofuranosyl linkages with 1-4 arabinofuranosides are also found in the sugar chains of extensin and solanaceous lectins, hydroxyproline (Hyp)2-rich glycoproteins that are widely observed in plant cell wall fractions. The critical residue for catalytic activity is Glu-338, in a ET/SCAS sequence context. |
| COG3533 | COG3533 | 6.19e-79 | 6 | 549 | 28 | 517 | Uncharacterized conserved protein, DUF1680 family [Function unknown]. |
| pfam07554 | FIVAR | 2.38e-05 | 680 | 728 | 1 | 55 | FIVAR domain. This domain is found in a wide variety of contexts, but mostly occurring in cell wall associated proteins. A lack of conserved catalytic residues suggests that it is a binding domain. From context, possible substrates are hyaluronate or fibronectin (personal obs: C Yeats). This is further evidenced by. Possibly the exact substrate is N-acetyl glucosamine. Finding it in the same protein as pfam05089 further supports this proposal. It is found in the C-terminal part of Bacillus sp. Gellan lyase, which is removed during maturation. Some of the proteins it is found in are involved in methicillin resistance. The name FIVAR derives from Found In Various Architectures. |
| TIGR04320 | Surf_Exclu_PgrA | 3.65e-05 | 635 | 726 | 264 | 350 | SEC10/PgrA surface exclusion domain. This model describes a conserved domain found in surface proteins of a number of Firmutes. Many members have LPXTG C-terminal anchoring motifs and a substantial number have the KxYKxGKxW putative sorting signal at the N-terminus. The tetracycline resistance plasmid pCF10 in Enterococcus faecalis promotes conjugal plasmid transfer in response to sex pheromones, but PgrA/Sec10 encoded by that plasmid, a member of this family, specifically inhibits the ability of cells to receive homologous plasmids. The phenomenon is called surface exclusion. |
| pfam07554 | FIVAR | 3.87e-04 | 613 | 671 | 2 | 67 | FIVAR domain. This domain is found in a wide variety of contexts, but mostly occurring in cell wall associated proteins. A lack of conserved catalytic residues suggests that it is a binding domain. From context, possible substrates are hyaluronate or fibronectin (personal obs: C Yeats). This is further evidenced by. Possibly the exact substrate is N-acetyl glucosamine. Finding it in the same protein as pfam05089 further supports this proposal. It is found in the C-terminal part of Bacillus sp. Gellan lyase, which is removed during maturation. Some of the proteins it is found in are involved in methicillin resistance. The name FIVAR derives from Found In Various Architectures. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBF45278.1 | 4.89e-243 | 2 | 602 | 548 | 1138 |
| AKA69367.1 | 6.36e-170 | 3 | 604 | 661 | 1215 |
| AWI04506.1 | 1.25e-169 | 3 | 604 | 661 | 1215 |
| AET60941.1 | 7.06e-151 | 1 | 602 | 211 | 765 |
| ASR47498.1 | 1.19e-149 | 1 | 602 | 211 | 765 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6YQH_AAA | 2.93e-81 | 4 | 601 | 47 | 649 | ChainAAA, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, biotin carboxylase [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 5OPJ_A | 3.62e-78 | 4 | 535 | 47 | 559 | Beta-L-arabinofuranosidase[Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron] |
| 6EX6_A | 1.54e-26 | 124 | 557 | 123 | 563 | TheGH127, Beta-arabinofuranosidase, BT3674 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],6EX6_B The GH127, Beta-arabinofuranosidase, BT3674 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 5MQO_A | 1.50e-16 | 152 | 507 | 247 | 577 | Glycosidehydrolase BT_1003 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
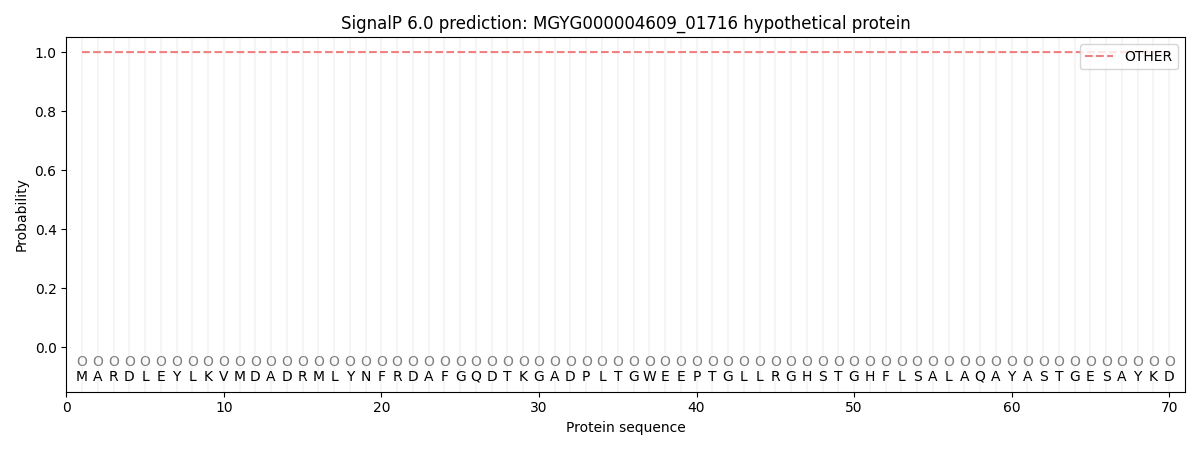
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000070 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |