You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004886_01230
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004886_01230
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Actinobacteriota; Actinomycetia; Actinomycetales; Micrococcaceae; Rothia; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004886_01230 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Resuscitation-promoting factor Rpf | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 169; End: 894 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam06737 | Transglycosylas | 1.15e-31 | 32 | 103 | 1 | 75 | Transglycosylase-like domain. This family of proteins are very likely to act as transglycosylase enzymes related to pfam00062 and pfam01464. These other families are weakly matched by this family, and include the known active site residues. |
| cd13925 | RPF | 1.30e-28 | 34 | 103 | 1 | 71 | core lysozyme-like domain of resuscitation-promoting factor proteins. Resuscitation-promoting factor (RPF) proteins, found in various (G+C)-rich Gram-positive bacteria, act to reactivate cultures from stationary phase. This protein shares elements of the structural core of lysozyme and related proteins. Furthermore, it shares a conserved active site glutamate which is required for activity, and has a polysaccharide binding cleft that corresponds to the peptidoglycan binding cleft of lysozyme. Muralytic activity of Rpf in Micrococcus luteus correlates with resuscitation, supporting a mechanism dependent on cleavage of peptidoglycan by RPF. |
| PRK11198 | PRK11198 | 2.74e-10 | 193 | 241 | 98 | 147 | LysM domain/BON superfamily protein; Provisional |
| cd00118 | LysM | 1.65e-09 | 192 | 239 | 2 | 45 | Lysin Motif is a small domain involved in binding peptidoglycan. LysM, a small globular domain with approximately 40 amino acids, is a widespread protein module involved in binding peptidoglycan in bacteria and chitin in eukaryotes. The domain was originally identified in enzymes that degrade bacterial cell walls, but proteins involved in many other biological functions also contain this domain. It has been reported that the LysM domain functions as a signal for specific plant-bacteria recognition in bacterial pathogenesis. Many of these enzymes are modular and are composed of catalytic units linked to one or several repeats of LysM domains. LysM domains are found in bacteria and eukaryotes. |
| pfam01476 | LysM | 1.87e-09 | 193 | 240 | 1 | 43 | LysM domain. The LysM (lysin motif) domain is about 40 residues long. It is found in a variety of enzymes involved in bacterial cell wall degradation. This domain may have a general peptidoglycan binding function. The structure of this domain is known. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAS19583.1 | 3.03e-124 | 1 | 241 | 1 | 250 |
| ATF62748.1 | 7.52e-124 | 1 | 241 | 1 | 256 |
| QXW98927.1 | 1.14e-117 | 1 | 241 | 1 | 252 |
| BAI65360.1 | 9.62e-113 | 1 | 241 | 1 | 256 |
| QQT89663.1 | 2.49e-86 | 1 | 241 | 1 | 244 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4CGE_A | 1.93e-25 | 36 | 106 | 4 | 74 | ChainA, Resuscitation-promoting Factor Rpfe [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4CGE_B Chain B, Resuscitation-promoting Factor Rpfe [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4CGE_C Chain C, Resuscitation-promoting Factor Rpfe [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4CGE_D Chain D, Resuscitation-promoting Factor Rpfe [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4CGE_E Chain E, Resuscitation-promoting Factor Rpfe [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4CGE_F Chain F, Resuscitation-promoting Factor Rpfe [Mycobacterium tuberculosis] |
| 2N5Z_A | 2.34e-25 | 36 | 109 | 9 | 82 | Mycobacteriumtuberculosis: a dynamic view of the resuscitation promoting factor RpfC catalytic domain [Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv] |
| 4OW1_A | 3.09e-25 | 36 | 109 | 6 | 79 | ChainA, Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4OW1_B Chain B, Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4OW1_E Chain E, Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4OW1_S Chain S, Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4OW1_T Chain T, Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4OW1_U Chain U, Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4OW1_W Chain W, Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC [Mycobacterium tuberculosis],4OW1_X Chain X, Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC [Mycobacterium tuberculosis] |
| 1XSF_A | 1.14e-22 | 31 | 108 | 26 | 106 | ChainA, Probable resuscitation-promoting factor rpfB [Mycobacterium tuberculosis] |
| 3EO5_A | 5.91e-22 | 31 | 108 | 89 | 169 | ChainA, Resuscitation-promoting factor rpfB [Mycobacterium tuberculosis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O86308 | 3.10e-30 | 4 | 240 | 12 | 221 | Resuscitation-promoting factor Rpf OS=Micrococcus luteus OX=1270 GN=rpf PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q6M6W5 | 1.22e-28 | 2 | 144 | 7 | 153 | Resuscitation-promoting factor Rpf1 OS=Corynebacterium glutamicum (strain ATCC 13032 / DSM 20300 / BCRC 11384 / JCM 1318 / LMG 3730 / NCIMB 10025) OX=196627 GN=rpf1 PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q6M6N7 | 8.29e-25 | 21 | 109 | 282 | 373 | Resuscitation-promoting factor Rpf2 OS=Corynebacterium glutamicum (strain ATCC 13032 / DSM 20300 / BCRC 11384 / JCM 1318 / LMG 3730 / NCIMB 10025) OX=196627 GN=rpf2 PE=1 SV=1 |
| H8F3N4 | 8.32e-25 | 17 | 109 | 16 | 110 | Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC OS=Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 35801 / TMC 107 / Erdman) OX=652616 GN=rpfC PE=2 SV=1 |
| O07747 | 2.14e-24 | 17 | 109 | 52 | 146 | Resuscitation-promoting factor RpfC OS=Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv) OX=83332 GN=rpfC PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
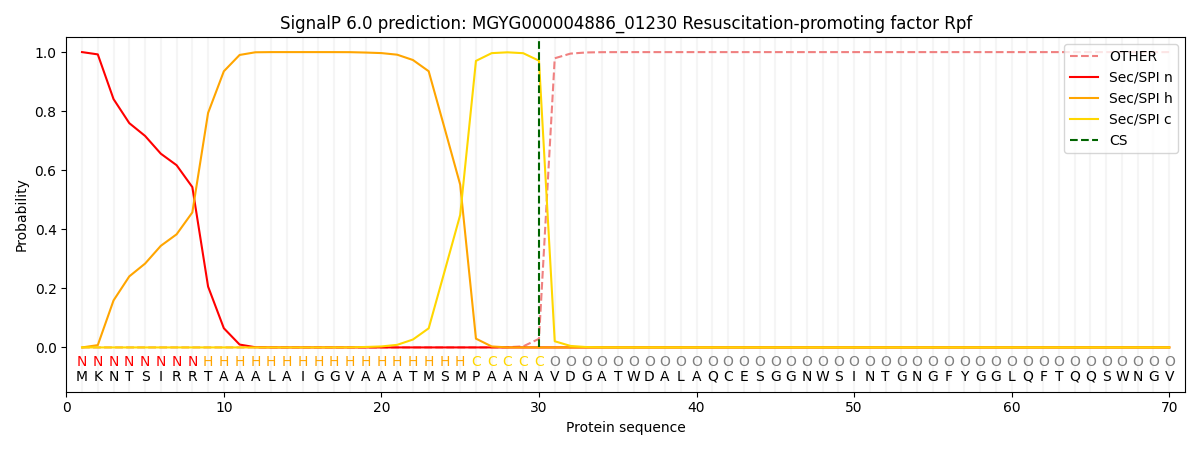
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000298 | 0.998852 | 0.000185 | 0.000272 | 0.000197 | 0.000173 |
