The most recent Pfam release (30.0) contains 16,306 families (http://pfam.xfam.org/). Among these families, 5,423 (33.3%) families are assigned to 595 clans. Among these clans, 254 (42.7%) clans have 5 or more families and 20 have over 40 families.
According to (Finn, et al., 2016), the graphical representation of clans with over 40 members has been a challenge. The most recent Pfam release attempted to address the issue using a new JavaScript clanviewer (Finn, et al., 2016) to present the families of a clan. Our experience is that such a network-like flash animated graph still does not work for well those large clans. With pHMM-tree, we have built phylogenies for the 254 clans with at least 5 families. All the trees could be viewed in our website. In the following, we selected two example clans to show the phylogenies.
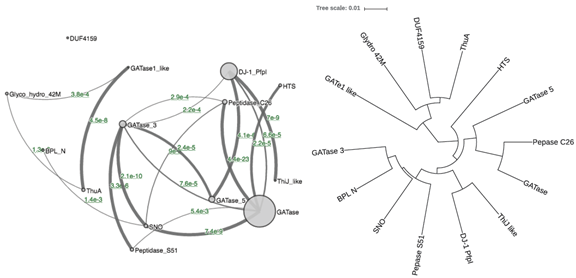
The first example is the Pfam clan Glutaminase_I (CL0014), which has 14 families. shows two representations of the family relationship of the clan. The left is the clanviewer network graph, with circles representing families and edges representing their relationships. The size of each circle represents the size of the family and the width of the edge represents the similarity between two families. The graph can be dragged to rearrange the layout and can be zoomed in or out. The right side of the figure shows the pHMM phylogeny, which is a more classic way for presenting evolutionary relationship of different entities, such as species, genes, and here protein families. The two representations both present two major groups of families, but the phylogeny is clearly much easier to understand and interpret. By nature, it also presents the relationship among different families in a hierarchical way. In addition, all families are included rather than left out in the graph. For example, the DUF4159 family is not connected to any other families in the network graph, but is clustered with its closest relative ThuA family in the phylogeny graph.
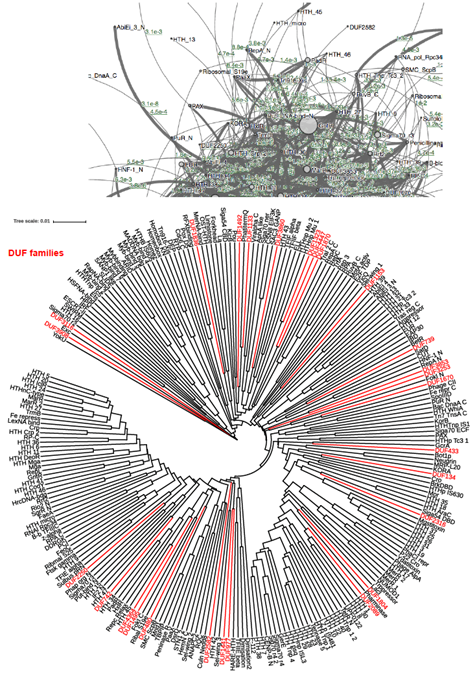
The second example is the largest Pfam clan CL0123 (Helix-turn-helix or HTH), which contains 254 families. As shown in Figure S8, the network graph is not possible to visualize in a global view as there are too many nodes and edges stacked on top of each other. Although clanviewer allows one to interactively view the graph (i.e., zoom in/out or move nodes by dragging), we believe the classic phylogenetic tree is much easier to view to capture the relationship among such as large number of families. As an example, we highlighted the 27 DUF (domain of unknown function) families in red in the phylogeny. One can quickly locate these families in the phylogeny and identify their closest neighbors.