

dbPUP is the first database to collect polyphenol utilization proteins that have been experimentally validated to catalyze or modify a polyphenol substrate. The database currently contains 60 proteins from gut microbiota that are manually curated from literature and enzyme database. These proteins have been characterized by different experimental approaches targeting one or more specific polyphenol substrates. These experimentally characterized proteins are also called seed proteins. Using these seed proteins, we also collected over 24,000 proteins that share conserved Pfam domains and significant sequence similarities with the seed proteins, and thus are potentially capable of metabolizing polyphenols. These proteins are also called computationally predicted proteins. All these seed proteins and computationally predicted proteins are compiled together and classified into protein families based on sequence homology and further categorized into classes according to EC numbers that the seed proteins have.
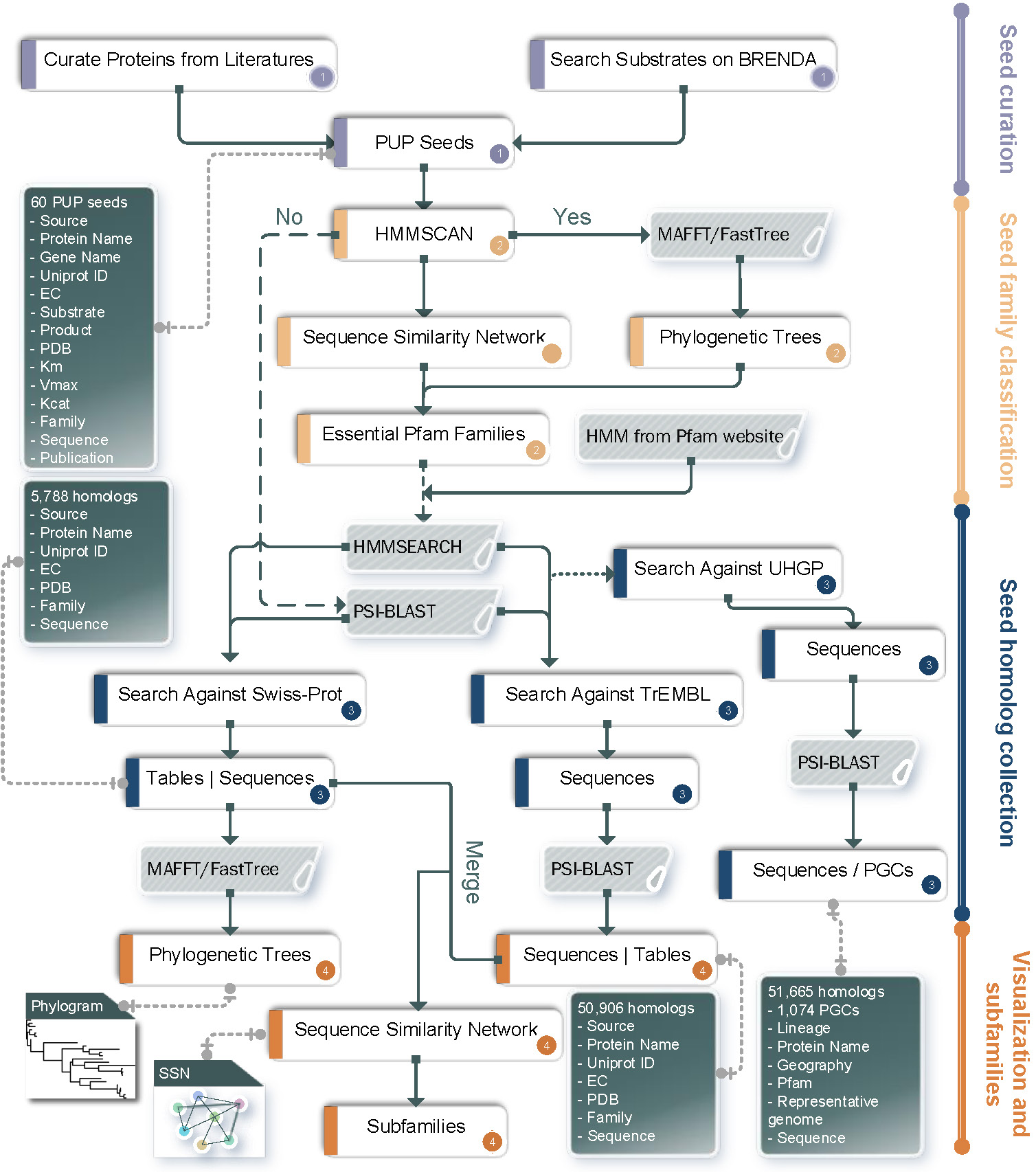
Workflow of dbPUP
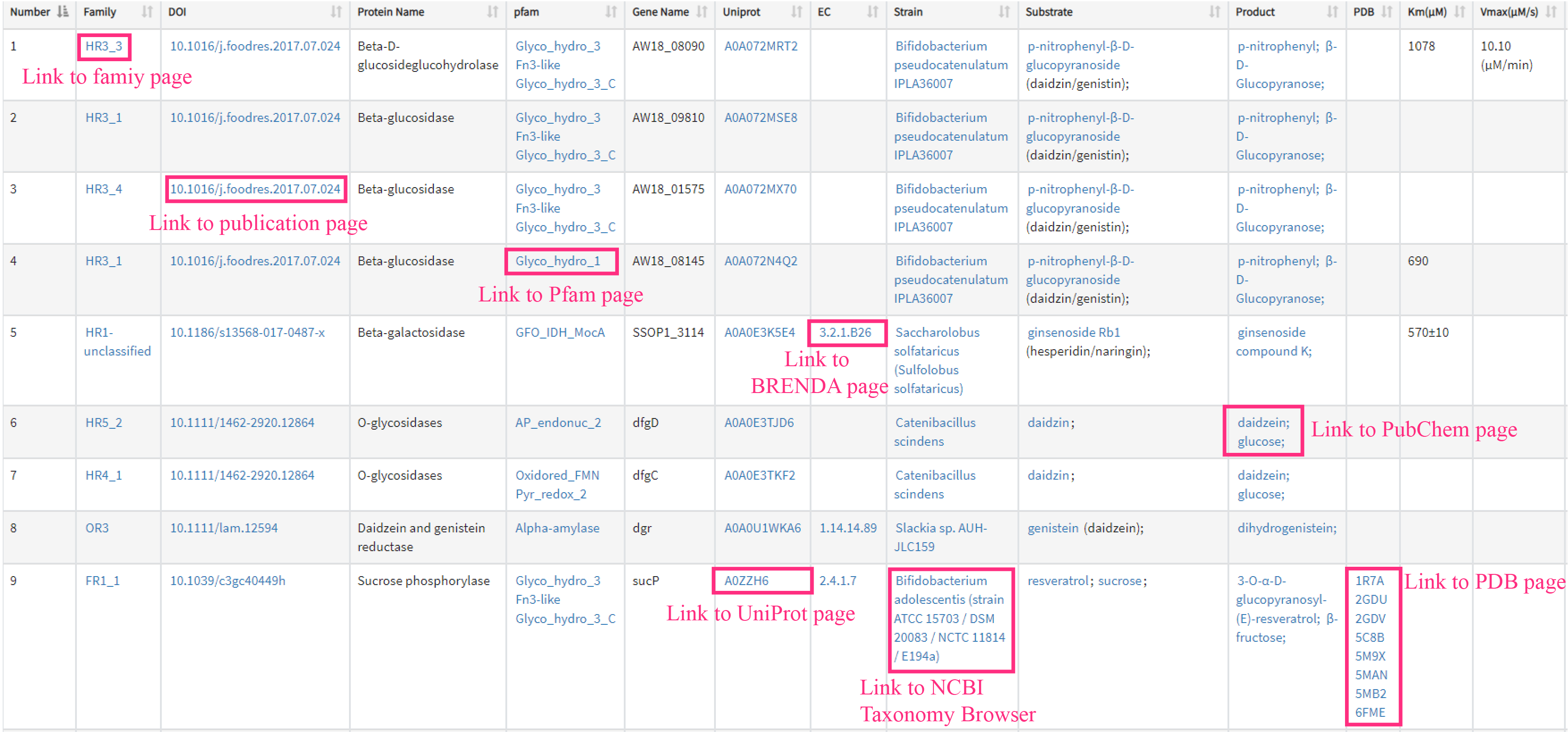
This page displays a table with all the seed proteins and associated metadata in dbPUP. Users can sort in ascending or descending order the number, strain, protein name, gene name, UniProt id, EC, substrate, product, PDB, Km, Vmax and Kcat.
Users can jump to a specific page looking for more details by clicking on blue text links in cell.
In the navigation menu, clicking on Class link will expand to show the list of classes. Clicking on each class will open the page of each enzyme class page, where users can find essential information about introduction, reaction description, Pfam of seeds, subfamily and EC. Clicking the Family name (e.g. OR1) will redirect users to Family page, where exhibits experimental results in very detail.
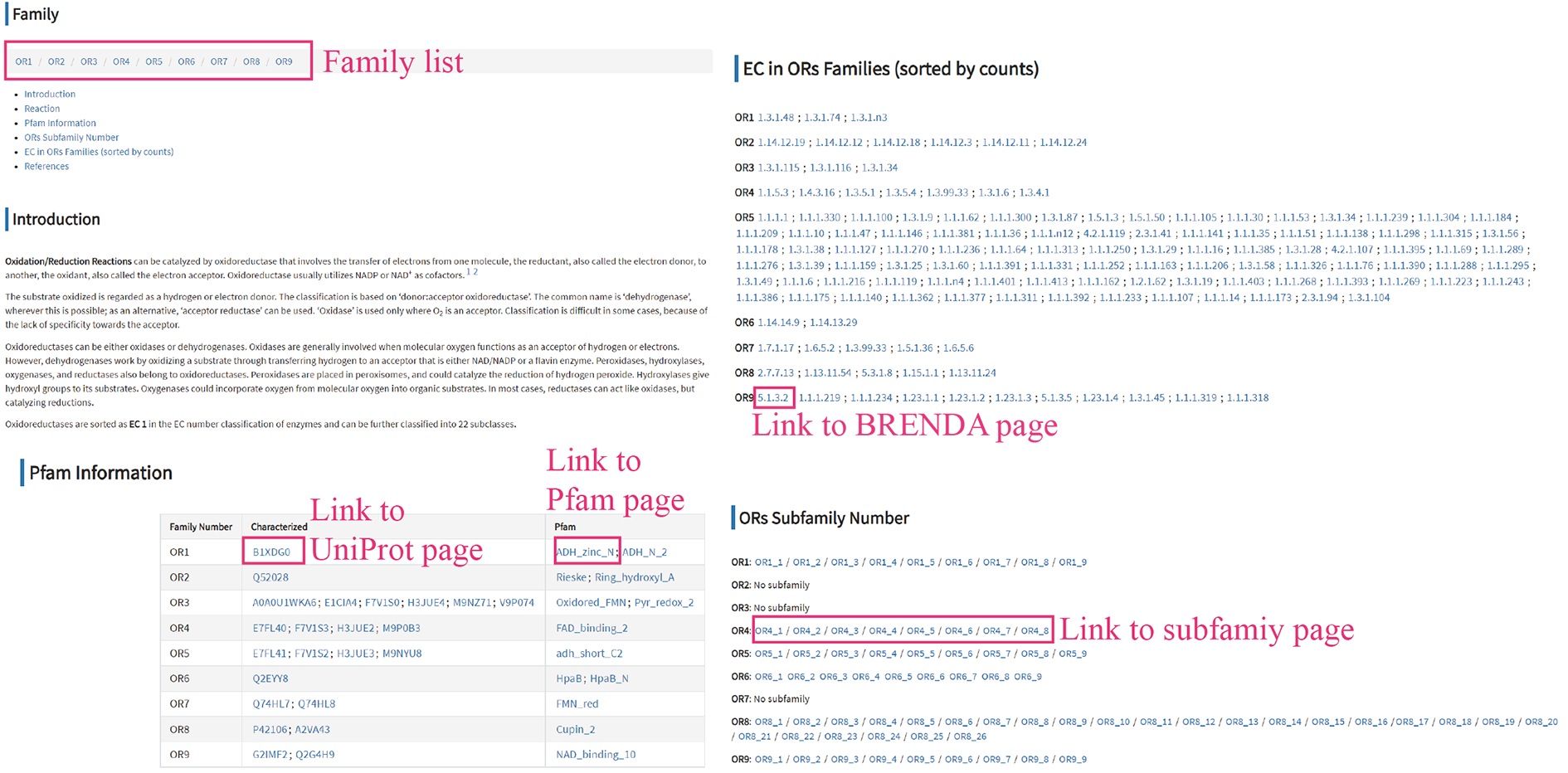
Each family have their corresponding Pfams and were extended by HMMSEARCH using raw HMM from Pfam website.
Metadata and general information about the seeds in this family, including literature information and Experimental results.
The Literature Information tab displays the title, authors, DOI and abstract of the corresponding publication. Polyphenols that involved in biochemical experiments are highlighted in abstract.

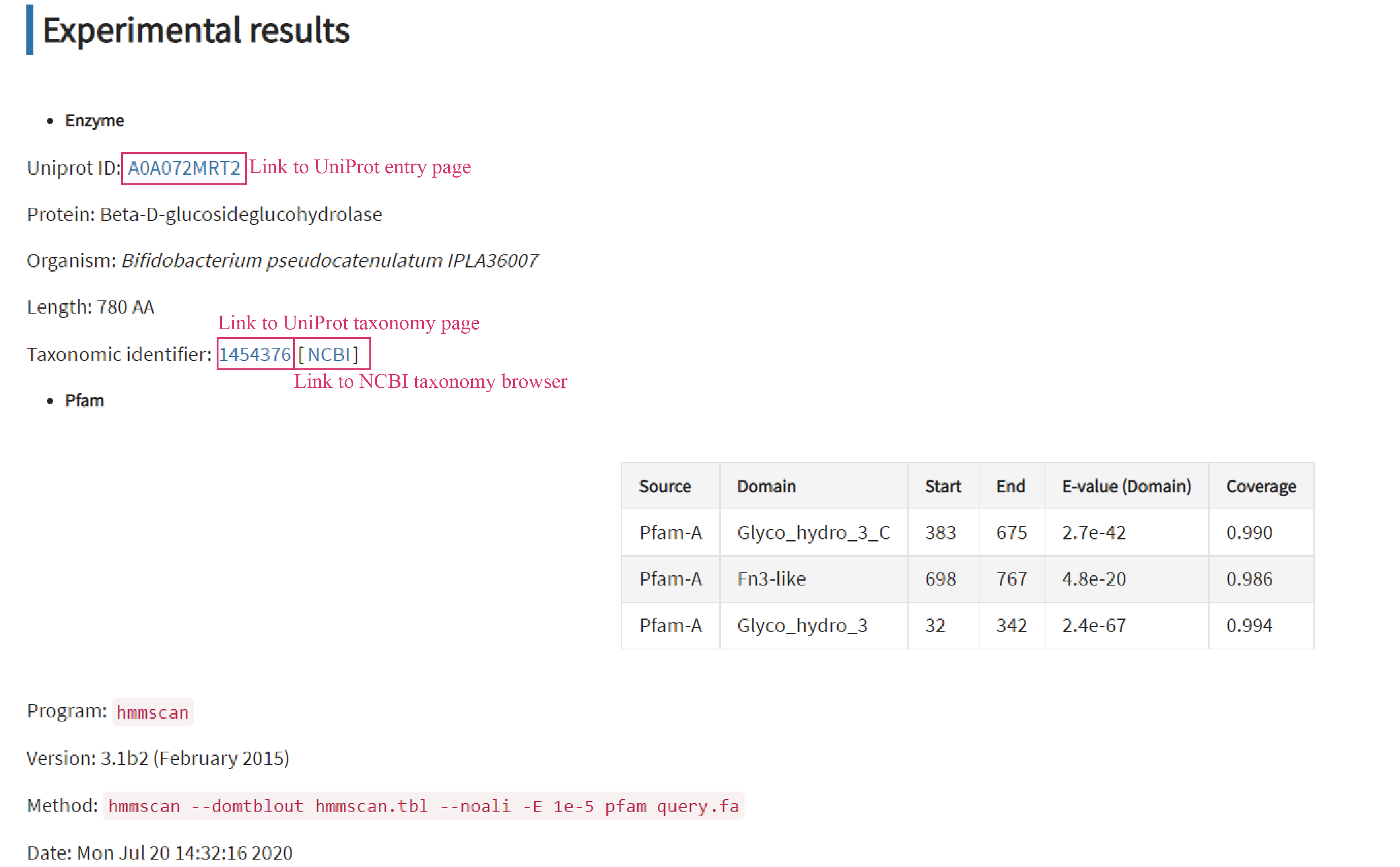
Experimental results tab displays the entry, Pfam and reaction information based on the above literature. Clicking blue text links redirects users to corresponding pages for more details.

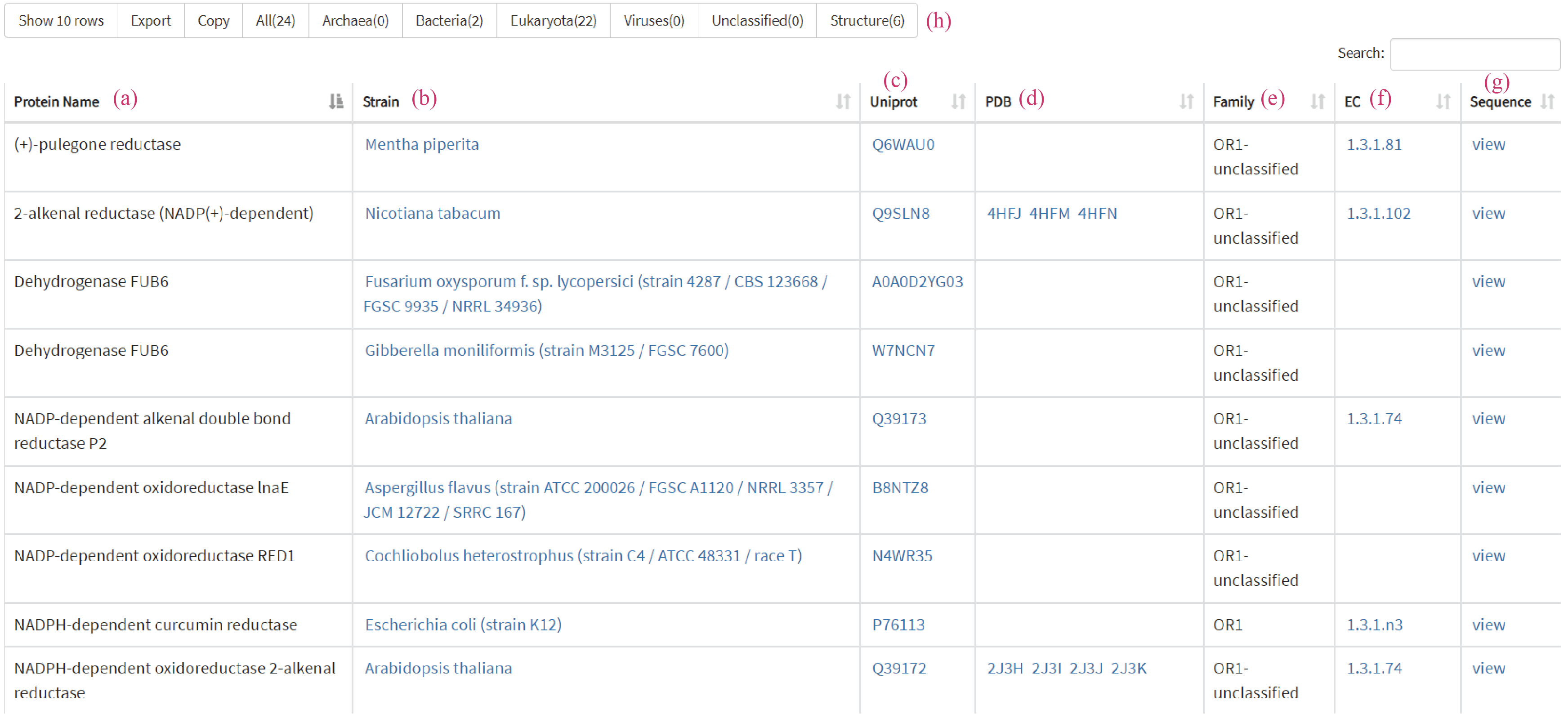
Both Swiss-Prot and TrEMBL tables consist of seven major parts of protein name (a), strain (b), UniProt (c), PDB (d), family (e), EC (f) and sequence (g). Users view the taxa of interest in same table by clicking the buttons (h) above the table.
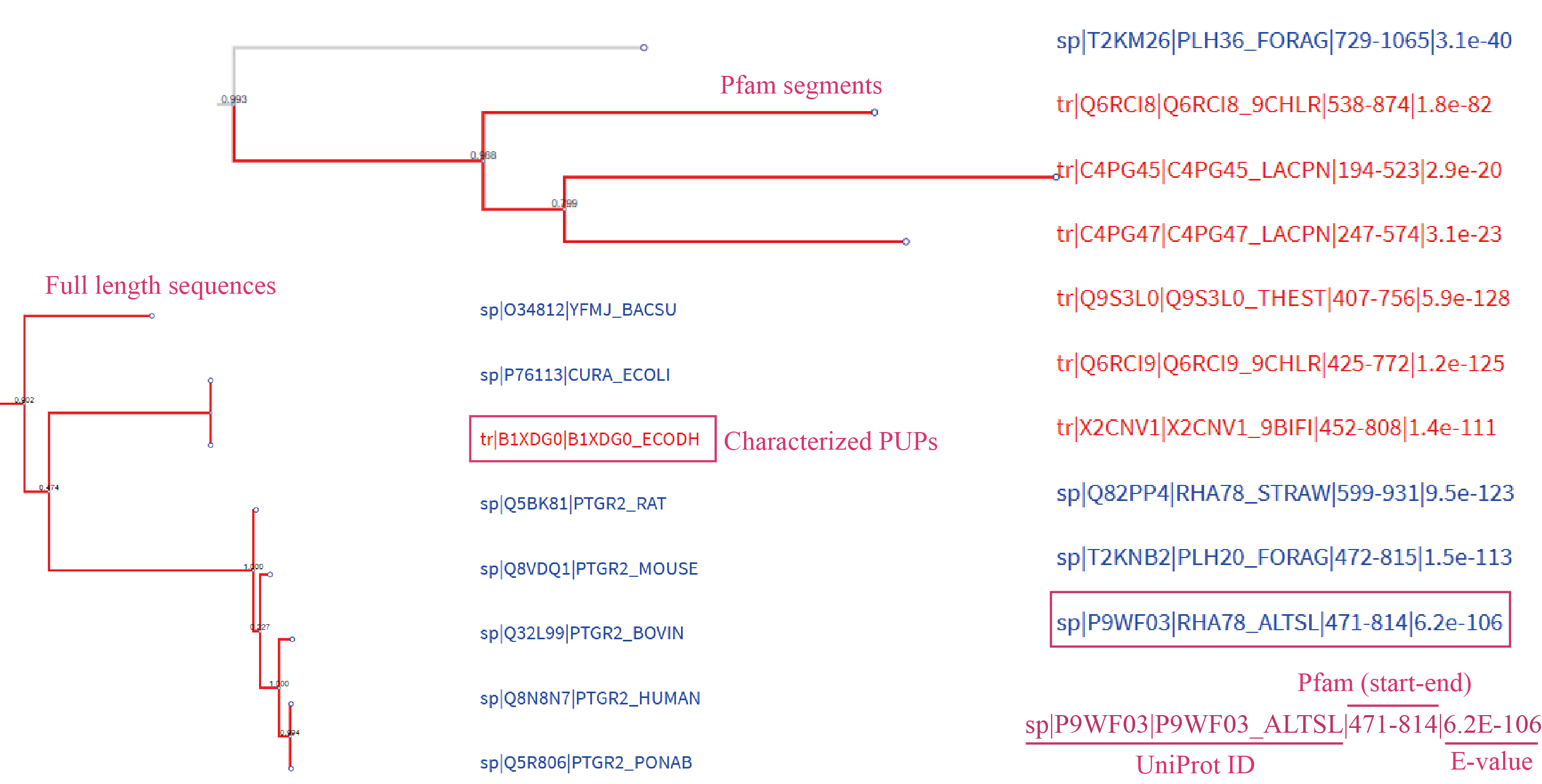
Family trait were totally depending on their seeds, which means sequences in a family should have all essential Pfams same with seeds. If seeds in a family only have one essential Pfam, the phylogenetic tree for this family will be constructed by sequence domain segments. However, for seeds have multiple essential Pfams, the phylogenetic tree were constructed by full length sequences.
Users can view a rectangular phylogenetic tree, if available, by clicking the tree button above the Swiss-Prot table. Features of the phylogenetic tree include:
Uses can find SSN visualization result for each family by clicking the network button above the TrEMBL table.
Two tabs with two figures are available. The first figure is an overview of all the sequences in this family. Usually, edges represent an E-value threshold below 10-80. Nodes in dark color indicate a subgroup containing seeds, while the light ones indicates individuals that distant with seeds.
The others are enlarged pictures for each subfamily. Nodes are filled by different color depending on their taxa. Additionally, nodes have a light yellow border indicate the seeds.

In the navigation menu, clicking on UHGP will open a new page, where users can find information about UHGP Hits list, UHGP introduction, UHGP homologs, physically linked PUP gene clusters (PGCs). The homologs found in UHGP-100 dataset are classified by continent, clicking the corresponding continent will redirect users to a new page, where present metadata about each homolog.
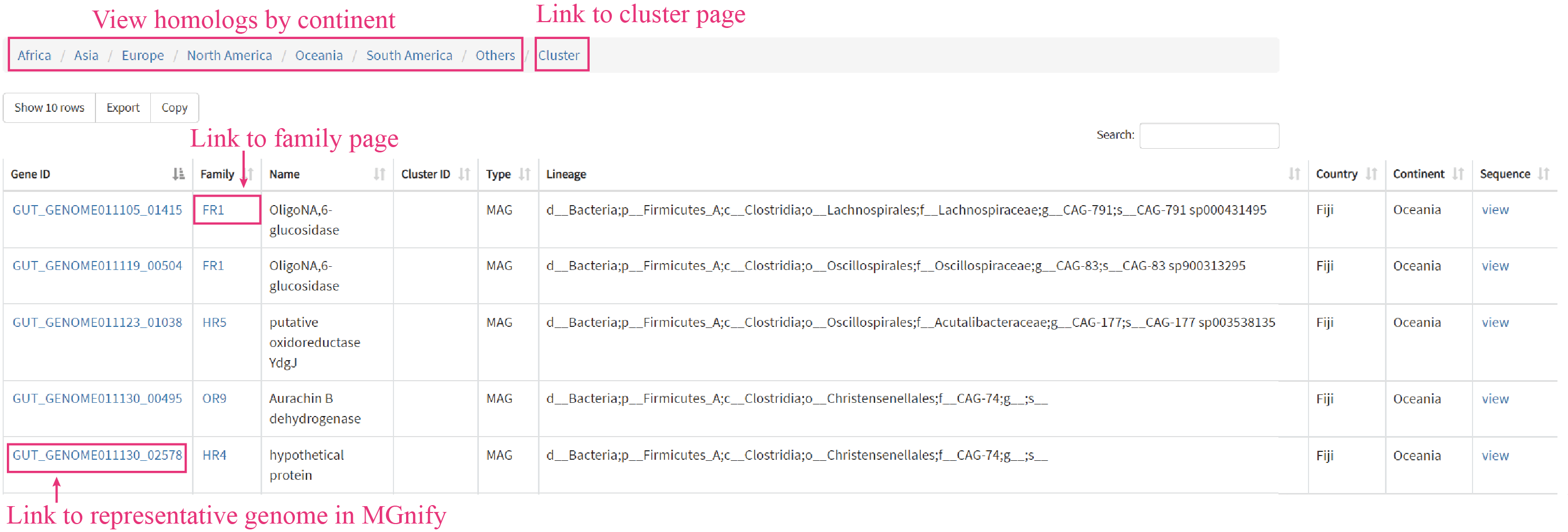
Users can browse the whole PGCs in tabular format by clicking the Cluster. The cluster ID will redirect the users to the corresponding PGC page, where exhibits the functional annotation about each gene in the PGC.
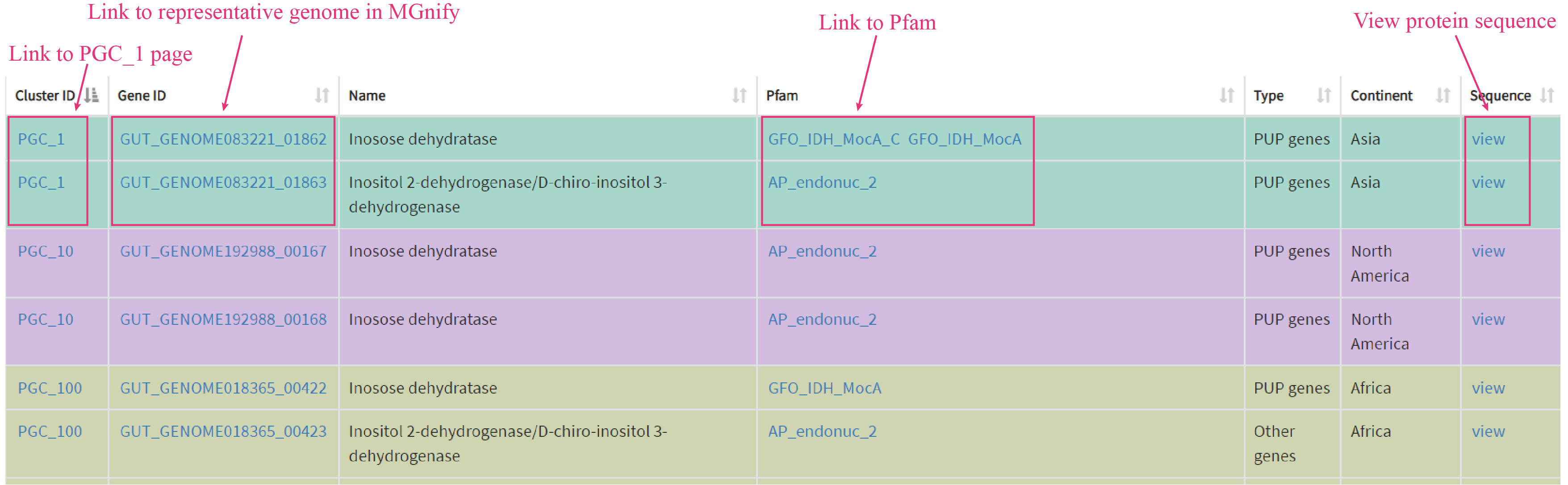

Clicking the Family name (e.g. OR1) will redirect users to Family page, where exhibits experimental results in very detail.
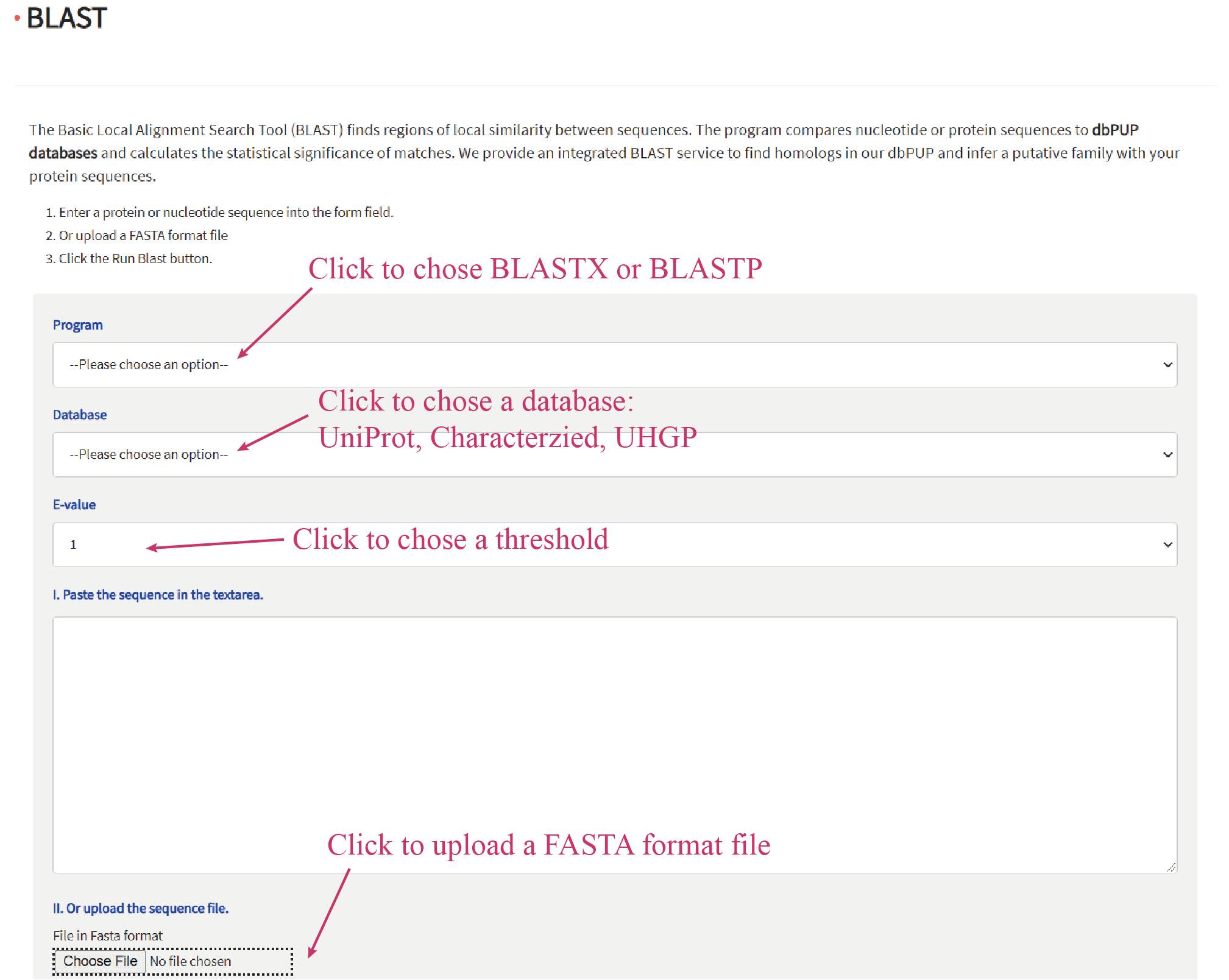
Users can enter a protein or nucleotide sequence of interest in FASTA format to perform a BLAST search against dbPUP. This can be done in following ways:
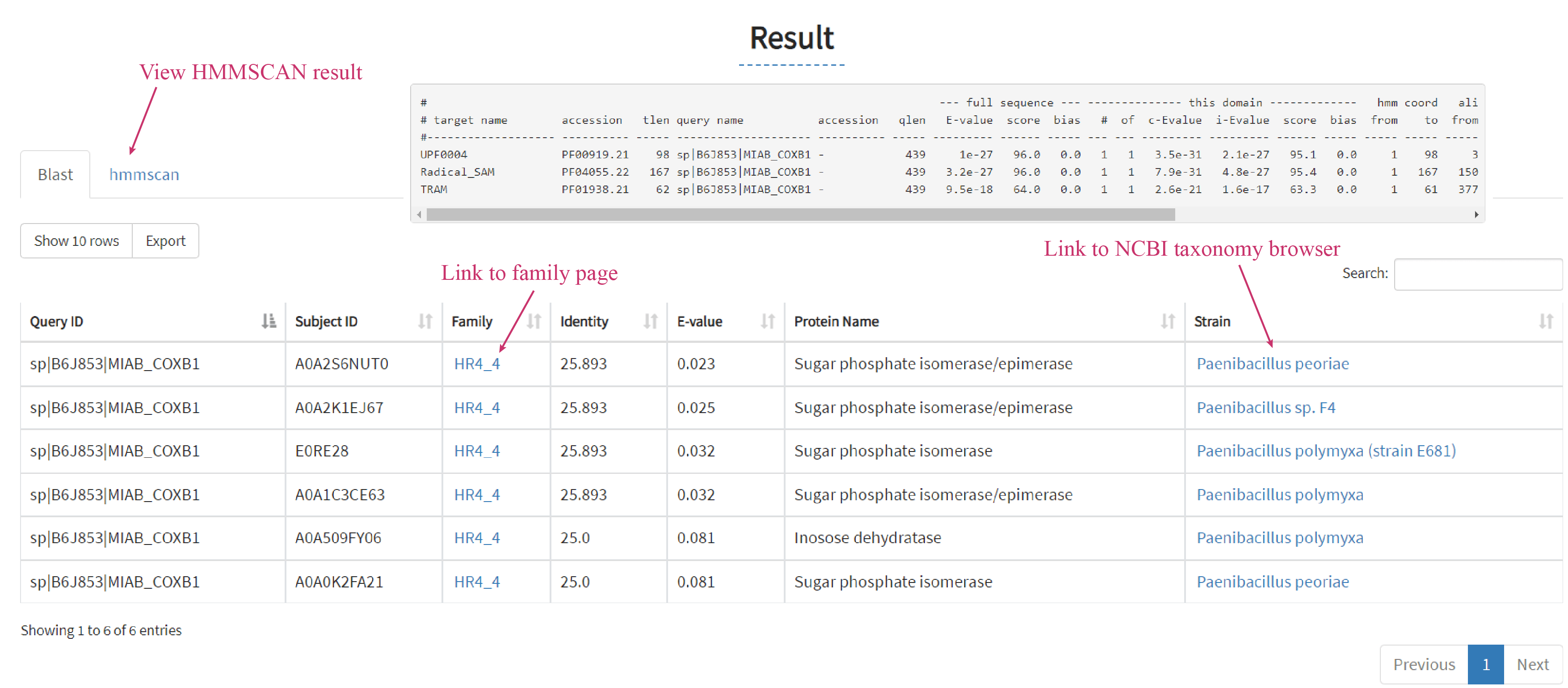
Results are displayed as a sortable table including hmmscan result (only applicable for protein sequence), protein information, scores, and E-values obtained from BLAST.
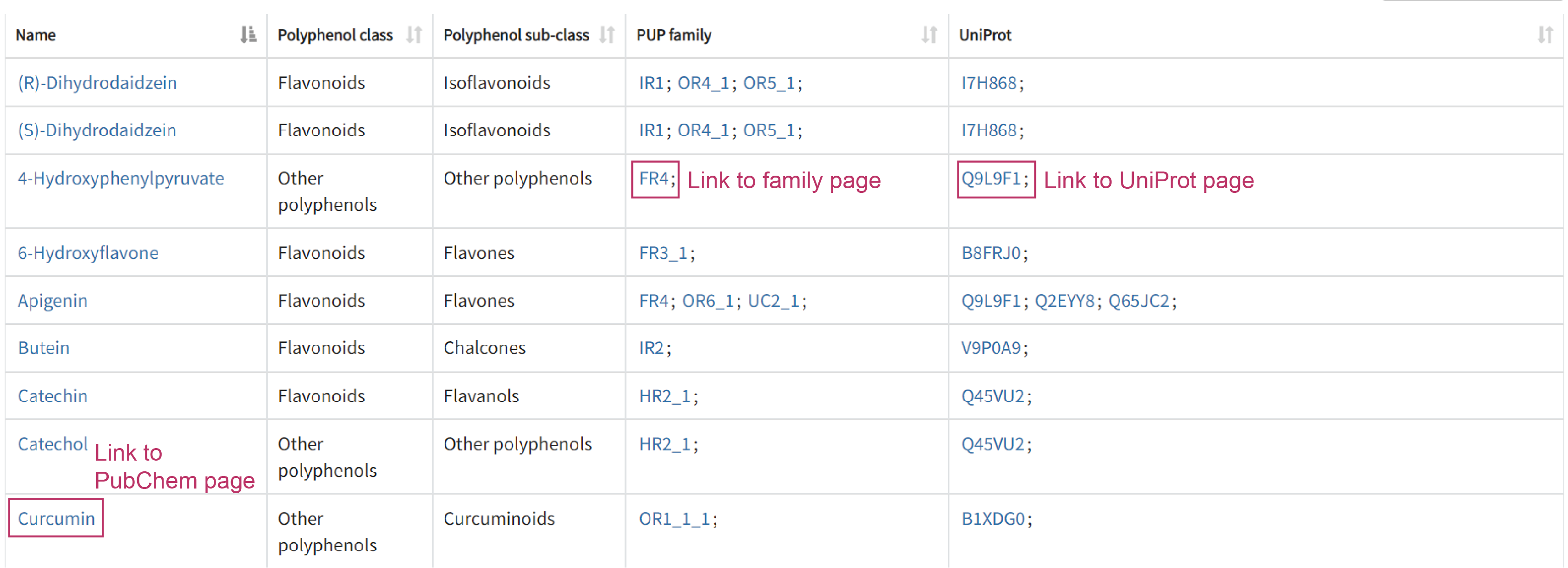
The Polyphenol page presents 47 polyphenols which are classified in 3 classes and 10 sub-classes (Rothwell, Joseph A., et al. Database 2013). Users can sort in ascending or descending order the name, polyphenol class, polyphenol sub-class, UniProt ID and associated PUP family. Clicking on the blue text link in cell will redirects users to specific page.
The Taxonomy page allows users to explore hierarchical data of taxonomic distribution of PUP homologs in dbPUP, with zooming, multi-layered pie charts.

All data for dbPUP are available for download. Data files for each zip file include:
PSI-BLAST results for each familyThe Statistics page includes a basic table about current data in dbPUP.